Example: Create a PyTorch Distributed KFP Step with the Kale SDK¶
This section will guide you through creating a PyTorch distributed KFP step on Kubeflow, using the Kale SDK and the Kubeflow Training Operator.
Overview
What You’ll Need¶
- An Arrikto EKF or MiniKF deployment with the default Kale Docker image.
- An understanding of how the Kale SDK works.
Procedure¶
Create a new Notebook server using the default Kale Docker image. The image will have the following naming scheme:
gcr.io/arrikto/jupyter-kale-py38:<IMAGE_TAG>Note
The
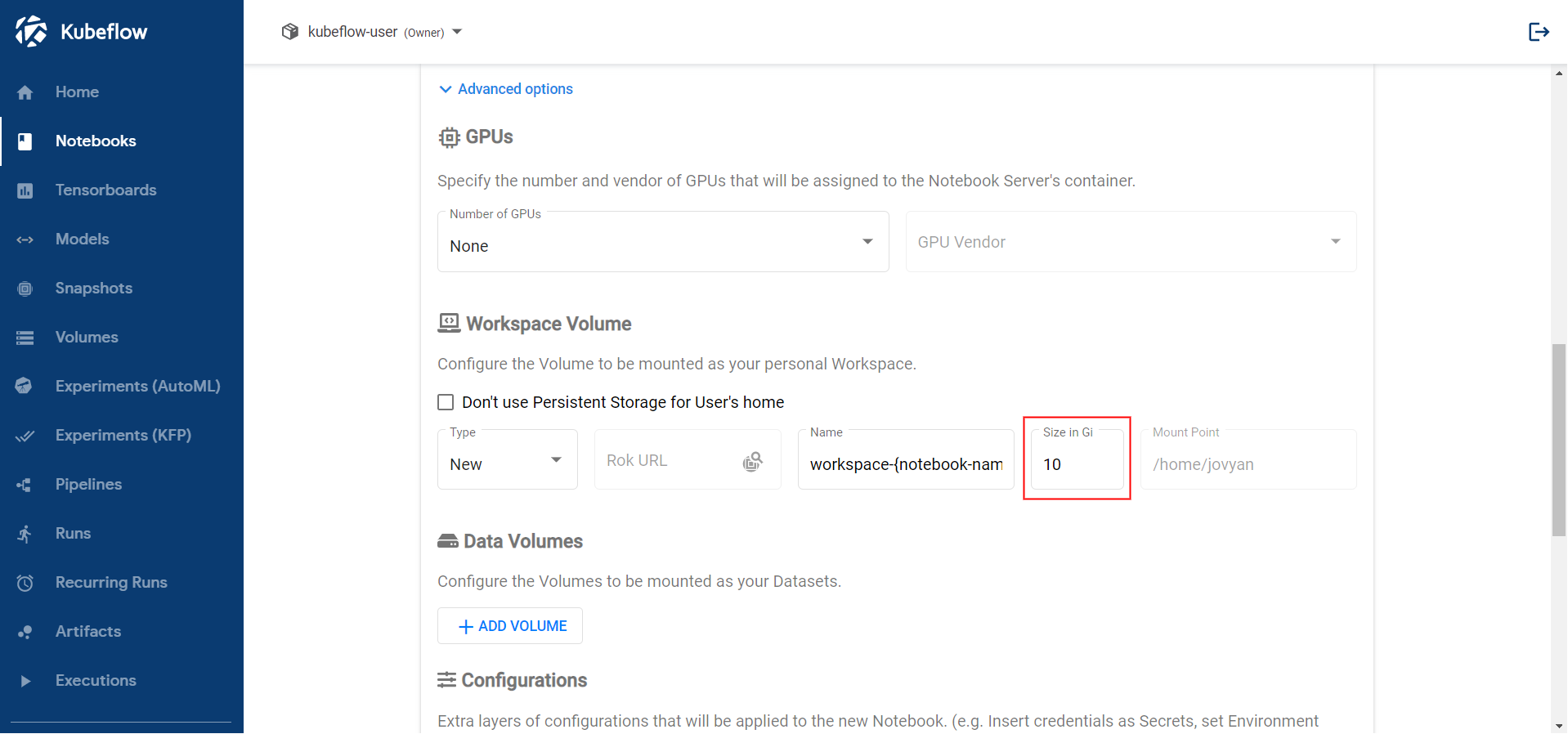
<IMAGE_TAG>varies based on the MiniKF or EKF release.Increase the size of the workspace volume to 10GB:
Connect to the server, open a terminal, and install the
torchandtorchvisionpackages:$ pip3 install --user torch==1.9.0+cu111 torchvision==0.10.0+cu111 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.htmlNote
The PyTorch version may be different. Please head to the PyTorch website for the latest releases.
Note
In this example, you will distribute the training job over multiple GPU devices. Thus, this command installs the CUDA version of the PyTorch package. If you are using CPU-only nodes, you can install the CPU-only version of the PyTorch package instead, and distribute the job over multiple CPU cores. You will see how to achieve that later in the user guide.
Create a new python file and name it
kale_dist.py:$ touch kale_dist.pyCopy and paste the following code inside
kale_dist.py:starter.py1 # Copyright © 2021 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 3 """Kale SDK. 4 5 This script creates a PyTorch distributed KFP step to solve Fashion MNIST. 6 """ 7 8 import torch 9 import torch.nn as nn 10 import torchvision.models as models 11 12 from torchvision import datasets 13 from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor 14 from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 15 16 from kale.sdk import pipeline, step 17 18 19 def _load_data(): 20 """Load and prepare the data.""" 21 train_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 22 root="/home/jovyan/data", 23 train=True, 24 download=True, 25 transform=ToTensor() 26 ) 27 28 valid_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 29 root="/home/jovyan/data", 30 train=False, 31 download=True, 32 transform=ToTensor() 33 ) 34 35 train_data_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=1024, shuffle=True) 36 valid_data_loader = DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=2014) 37 38 return train_data_loader, valid_data_loader 39 40 41 @step(name="create_model") 42 def create_model(): 43 """Define the model.""" 44 model = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) 45 model.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), 46 padding=(3, 3), bias=False) 47 48 for param in model.parameters(): 49 param.requires_grad = False 50 51 features_in = model.fc.in_features 52 model.fc = nn.Linear(features_in, 10) 53 54 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=.03) 55 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 56 57 return model, optimizer, criterion 58 59 60 @pipeline(name="fmnist", experiment="kale-dist") 61 def ml_pipeline(): 62 """Run the ML pipeline.""" 63 model, optimizer, criterion = create_model() 64 65 66 if __name__ == "__main__": 67 ml_pipeline() This script creates a pipeline with one step. This step creates a PyTorch model, an optimizer, and a criterion (i.e., loss function).
Important
Always use absolute paths when specifying the path to a file or folder. For example, in the
_load_datafunction, we specify where PyTorch should download the FashionMNIST dataset.Define the training and validation steps. The following snippet summarizes the changes in code:
steps.py1 # Copyright © 2021 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 3 """Kale SDK. 4-13 4 5 This script creates a PyTorch distributed KFP step to solve Fashion MNIST. 6 """ 7 8 import torch 9 import torch.nn as nn 10 import torchvision.models as models 11 12 from torchvision import datasets 13 from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor 14 from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 15 16 from kale.sdk import pipeline, step 17 + 18 + 19 + def _train_step(model, data_loader, criterion, optimizer, device, args): 20 + import logging 21 + 22 + log = logging.getLogger(__name__) 23 + 24 + for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(data_loader): 25 + features = features.to(device) 26 + labels = labels.to(device) 27 + 28 + pred = model(features) 29 + loss = criterion(pred, labels.reshape(-1)) 30 + 31 + loss.backward() 32 + 33 + optimizer.step() 34 + optimizer.zero_grad() 35 + 36 + if i % args.get("log_interval", 2) == 0: 37 + log.info("\tLoss = {}".format(loss.item())) 38 + 39 + return loss 40 + 41 + 42 + def _eval_step(model, data_loader, criterion, device, args): 43 + import logging 44 + 45 + log = logging.getLogger(__name__) 46 + 47 + for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(data_loader): 48 + features = features.to(device) 49 + labels = labels.to(device) 50 + 51 + pred = model(features) 52 + loss = criterion(pred, labels.reshape(-1)) 53 + 54 + log.info("\tLoss = {}".format(loss.item())) 55 + 56 + return loss 57 58 59 def _load_data(): 60-104 60 """Load and prepare the data.""" 61 train_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 62 root="/home/jovyan/data", 63 train=True, 64 download=True, 65 transform=ToTensor() 66 ) 67 68 valid_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 69 root="/home/jovyan/data", 70 train=False, 71 download=True, 72 transform=ToTensor() 73 ) 74 75 train_data_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=1024, shuffle=True) 76 valid_data_loader = DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=2014) 77 78 return train_data_loader, valid_data_loader 79 80 81 @step(name="create_model") 82 def create_model(): 83 """Define the model.""" 84 model = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) 85 model.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), 86 padding=(3, 3), bias=False) 87 88 for param in model.parameters(): 89 param.requires_grad = False 90 91 features_in = model.fc.in_features 92 model.fc = nn.Linear(features_in, 10) 93 94 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=.03) 95 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 96 97 return model, optimizer, criterion 98 99 100 @pipeline(name="fmnist", experiment="kale-dist") 101 def ml_pipeline(): 102 """Run the ML pipeline.""" 103 model, optimizer, criterion = create_model() 104 105 106 if __name__ == "__main__": 107 ml_pipeline() The
train_stepandvalid_stepfunctions are user-defined functions that dictate what happens during training. While you should provide atrain_stepfunction, thevalid_stepfunction is optional but highly recommended.Important
The
train_stepandvalid_stepfunctions must have exactly this signature and they must be standalone functions. This means that you should import all the Python modules the function depends on within its body and you must pass any extra arguments inside theargsdictionary.Distribute the training job over multiple GPU devices. The following snippet summarizes the changes in code:
pytorchjob.py1 # Copyright © 2021 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 3 """Kale SDK. 4-13 4 5 This script creates a PyTorch distributed KFP step to solve Fashion MNIST. 6 """ 7 8 import torch 9 import torch.nn as nn 10 import torchvision.models as models 11 12 from torchvision import datasets 13 from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor 14 from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 15 16 from kale.sdk import pipeline, step 17 + from kale.distributed import pytorch 18 19 20 def _train_step(model, data_loader, criterion, optimizer, device, args): 21-97 21 import logging 22 23 log = logging.getLogger(__name__) 24 25 for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(data_loader): 26 features = features.to(device) 27 labels = labels.to(device) 28 29 pred = model(features) 30 loss = criterion(pred, labels.reshape(-1)) 31 32 loss.backward() 33 34 optimizer.step() 35 optimizer.zero_grad() 36 37 if i % args.get("log_interval", 2) == 0: 38 log.info("\tLoss = {}".format(loss.item())) 39 40 return loss 41 42 43 def _eval_step(model, data_loader, criterion, device, args): 44 import logging 45 46 log = logging.getLogger(__name__) 47 48 for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(data_loader): 49 features = features.to(device) 50 labels = labels.to(device) 51 52 pred = model(features) 53 loss = criterion(pred, labels.reshape(-1)) 54 55 log.info("\tLoss = {}".format(loss.item())) 56 57 return loss 58 59 60 def _load_data(): 61 """Load and prepare the data.""" 62 train_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 63 root="/home/jovyan/data", 64 train=True, 65 download=True, 66 transform=ToTensor() 67 ) 68 69 valid_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 70 root="/home/jovyan/data", 71 train=False, 72 download=True, 73 transform=ToTensor() 74 ) 75 76 train_data_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=1024, shuffle=True) 77 valid_data_loader = DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=2014) 78 79 return train_data_loader, valid_data_loader 80 81 82 @step(name="create_model") 83 def create_model(): 84 """Define the model.""" 85 model = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) 86 model.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), 87 padding=(3, 3), bias=False) 88 89 for param in model.parameters(): 90 param.requires_grad = False 91 92 features_in = model.fc.in_features 93 model.fc = nn.Linear(features_in, 10) 94 95 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=.03) 96 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 97 98 return model, optimizer, criterion 99 100 101 + @step(name="model_training") 102 + def distribute_training(model, optimizer, criterion): 103 + """Train the model.""" 104 + train_data_loader, valid_data_loader = _load_data() 105 + job = pytorch.distribute(model, 106 + train_data_loader, 107 + criterion, 108 + optimizer, 109 + _train_step, 110 + eval_data_loader=valid_data_loader, 111 + eval_step=_eval_step, 112 + epochs=1, 113 + number_of_processes=2, 114 + cuda=True, 115 + train_args={"log_interval": 2}) 116 + 117 + return job.name 118 + 119 + 120 @pipeline(name="fmnist", experiment="kale-dist") 121 def ml_pipeline(): 122 """Run the ML pipeline.""" 123 model, optimizer, criterion = create_model() 124 + distribute_training(model, optimizer, criterion) 125 126 127 if __name__ == "__main__": 128 ml_pipeline() To find out more about the process the
distributefunction follows, head to the corresponding section of the PyTorch distributed with Kale guide.Important
You should create the PyTorch
DataLoaderinside the same step that launches the training job. This is a limitation due to the way Kale handles the serialization of those assets. In future versions we plan to remove this limitation.Important
If you need to use a custom PyTorch
Dataset, by subclassing thetorch.utils.data.Datasetclass, you need to keep your class definition inside this Python script, at module-level scope. This is a limitation due to the way Kale handles the serialization of those assets.Note
If you want to distribute your model across multiple CPU cores, you can set the
cudaargument toFalse. By default, Kale will launch two processes (the minimum number of processes required by thePyTorchJobCR), on two different GPU devices.Monitor the
PyTorchJobCR you submitted. The following snippet summarizes the changes in code:final.py1 - # Copyright © 2021 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 + # Copyright © 2021-2022 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 3 4 """Kale SDK. 5 6 This script creates a PyTorch distributed KFP step to solve Fashion MNIST. 7 """ 8 9 + import time 10 import torch 11 import torch.nn as nn 12 import torchvision.models as models 13-13 13 14 from torchvision import datasets 15 from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor 16 from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 17 + from rok_kubernetes.exceptions import ApiException 18 19 from kale.sdk import pipeline, step 20 from kale.distributed import pytorch 21-119 21 22 23 def _train_step(model, data_loader, criterion, optimizer, device, args): 24 import logging 25 26 log = logging.getLogger(__name__) 27 28 for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(data_loader): 29 features = features.to(device) 30 labels = labels.to(device) 31 32 pred = model(features) 33 loss = criterion(pred, labels.reshape(-1)) 34 35 loss.backward() 36 37 optimizer.step() 38 optimizer.zero_grad() 39 40 if i % args.get("log_interval", 2) == 0: 41 log.info("\tLoss = {}".format(loss.item())) 42 43 return loss 44 45 46 def _eval_step(model, data_loader, criterion, device, args): 47 import logging 48 49 log = logging.getLogger(__name__) 50 51 for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(data_loader): 52 features = features.to(device) 53 labels = labels.to(device) 54 55 pred = model(features) 56 loss = criterion(pred, labels.reshape(-1)) 57 58 log.info("\tLoss = {}".format(loss.item())) 59 60 return loss 61 62 63 def _load_data(): 64 """Load and prepare the data.""" 65 train_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 66 root="/home/jovyan/data", 67 train=True, 68 download=True, 69 transform=ToTensor() 70 ) 71 72 valid_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 73 root="/home/jovyan/data", 74 train=False, 75 download=True, 76 transform=ToTensor() 77 ) 78 79 train_data_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=1024, shuffle=True) 80 valid_data_loader = DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=2014) 81 82 return train_data_loader, valid_data_loader 83 84 85 @step(name="create_model") 86 def create_model(): 87 """Define the model.""" 88 model = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) 89 model.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), 90 padding=(3, 3), bias=False) 91 92 for param in model.parameters(): 93 param.requires_grad = False 94 95 features_in = model.fc.in_features 96 model.fc = nn.Linear(features_in, 10) 97 98 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=.03) 99 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 100 101 return model, optimizer, criterion 102 103 104 @step(name="model_training") 105 def distribute_training(model, optimizer, criterion): 106 """Train the model.""" 107 train_data_loader, valid_data_loader = _load_data() 108 job = pytorch.distribute(model, 109 train_data_loader, 110 criterion, 111 optimizer, 112 _train_step, 113 eval_data_loader=valid_data_loader, 114 eval_step=_eval_step, 115 epochs=1, 116 number_of_processes=2, 117 cuda=True, 118 train_args={"log_interval": 2}) 119 120 return job.name 121 122 123 + @step(name="monitor") 124 + def monitor(name): 125 + """Monitor the PyTorchJob CR.""" 126 + job = pytorch.PyTorchJob(name) 127 + while True: # Iterate if streaming logs raises an ApiException 128 + while True: 129 + cr = job.get() 130 + if (job.get_job_status() not in ["", "Created", "Restarting"] 131 + and (cr.get("status", {}) 132 + .get("replicaStatuses", {}) 133 + .get("Master", {}))): 134 + break 135 + print("Job pending...") 136 + time.sleep(2) 137 + try: 138 + job.stream_logs() 139 + break 140 + except ApiException as e: 141 + print("Streaming the logs failed with: %s" % str(e)) 142 + print("Retrying...") 143 + 144 + 145 @pipeline(name="fmnist", experiment="kale-dist") 146 def ml_pipeline(): 147 """Run the ML pipeline.""" 148 model, optimizer, criterion = create_model() 149 - distribute_training(model, optimizer, criterion) 150 + name = distribute_training(model, optimizer, criterion) 151 + monitor(name) 152 153 154 if __name__ == "__main__": 155 ml_pipeline() Optional
Delete the
PyTorchJobCR after completion. The following snippet summarizes the changes in code:delete.py1 # Copyright © 2021-2022 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 3 """Kale SDK. 4-140 4 5 This script creates a PyTorch distributed KFP step to solve Fashion MNIST. 6 """ 7 8 import time 9 import torch 10 import torch.nn as nn 11 import torchvision.models as models 12 13 from torchvision import datasets 14 from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor 15 from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 16 from rok_kubernetes.exceptions import ApiException 17 18 from kale.sdk import pipeline, step 19 from kale.distributed import pytorch 20 21 22 def _train_step(model, data_loader, criterion, optimizer, device, args): 23 import logging 24 25 log = logging.getLogger(__name__) 26 27 for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(data_loader): 28 features = features.to(device) 29 labels = labels.to(device) 30 31 pred = model(features) 32 loss = criterion(pred, labels.reshape(-1)) 33 34 loss.backward() 35 36 optimizer.step() 37 optimizer.zero_grad() 38 39 if i % args.get("log_interval", 2) == 0: 40 log.info("\tLoss = {}".format(loss.item())) 41 42 return loss 43 44 45 def _eval_step(model, data_loader, criterion, device, args): 46 import logging 47 48 log = logging.getLogger(__name__) 49 50 for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(data_loader): 51 features = features.to(device) 52 labels = labels.to(device) 53 54 pred = model(features) 55 loss = criterion(pred, labels.reshape(-1)) 56 57 log.info("\tLoss = {}".format(loss.item())) 58 59 return loss 60 61 62 def _load_data(): 63 """Load and prepare the data.""" 64 train_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 65 root="/home/jovyan/data", 66 train=True, 67 download=True, 68 transform=ToTensor() 69 ) 70 71 valid_data = datasets.FashionMNIST( 72 root="/home/jovyan/data", 73 train=False, 74 download=True, 75 transform=ToTensor() 76 ) 77 78 train_data_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=1024, shuffle=True) 79 valid_data_loader = DataLoader(valid_data, batch_size=2014) 80 81 return train_data_loader, valid_data_loader 82 83 84 @step(name="create_model") 85 def create_model(): 86 """Define the model.""" 87 model = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) 88 model.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), 89 padding=(3, 3), bias=False) 90 91 for param in model.parameters(): 92 param.requires_grad = False 93 94 features_in = model.fc.in_features 95 model.fc = nn.Linear(features_in, 10) 96 97 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=.03) 98 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 99 100 return model, optimizer, criterion 101 102 103 @step(name="model_training") 104 def distribute_training(model, optimizer, criterion): 105 """Train the model.""" 106 train_data_loader, valid_data_loader = _load_data() 107 job = pytorch.distribute(model, 108 train_data_loader, 109 criterion, 110 optimizer, 111 _train_step, 112 eval_data_loader=valid_data_loader, 113 eval_step=_eval_step, 114 epochs=1, 115 number_of_processes=2, 116 cuda=True, 117 train_args={"log_interval": 2}) 118 119 return job.name 120 121 122 @step(name="monitor") 123 def monitor(name): 124 """Monitor the PyTorchJob CR.""" 125 job = pytorch.PyTorchJob(name) 126 while True: # Iterate if streaming logs raises an ApiException 127 while True: 128 cr = job.get() 129 if (job.get_job_status() not in ["", "Created", "Restarting"] 130 and (cr.get("status", {}) 131 .get("replicaStatuses", {}) 132 .get("Master", {}))): 133 break 134 print("Job pending...") 135 time.sleep(2) 136 try: 137 job.stream_logs() 138 break 139 except ApiException as e: 140 print("Streaming the logs failed with: %s" % str(e)) 141 print("Retrying...") 142 143 144 + @step(name="delete") 145 + def delete(name): 146 + """Delete the PyTorchJob CR.""" 147 + job = pytorch.PyTorchJob(name) 148 + while job.get_job_status() != "Succeeded": 149 + continue 150 + job.delete() 151 + 152 + 153 @pipeline(name="fmnist", experiment="kale-dist") 154 def ml_pipeline(): 155 """Run the ML pipeline.""" 156 model, optimizer, criterion = create_model() 157 name = distribute_training(model, optimizer, criterion) 158 monitor(name) 159 + delete(name) 160 161 162 if __name__ == "__main__": 163 ml_pipeline() Important
After the completion of the training process the controller will not remove the resources it creates. If you do not want to leave stale resources you have to manually delete the CR.
Optional
Produce a workflow YAML file that you can inspect:
$ python3 -m kale kale_dist.py --compileDeploy and run your code as a KFP pipeline:
$ python3 -m kale kale_dist.py --kfpNote
To see the complete list of arguments and their respective usage, run
python3 -m kale --help.View the trained model by navigating to the KFP UI and selecting the
model_trainingstep. Kale logs the trained Pytorch model as an output MLMD artifact of that step: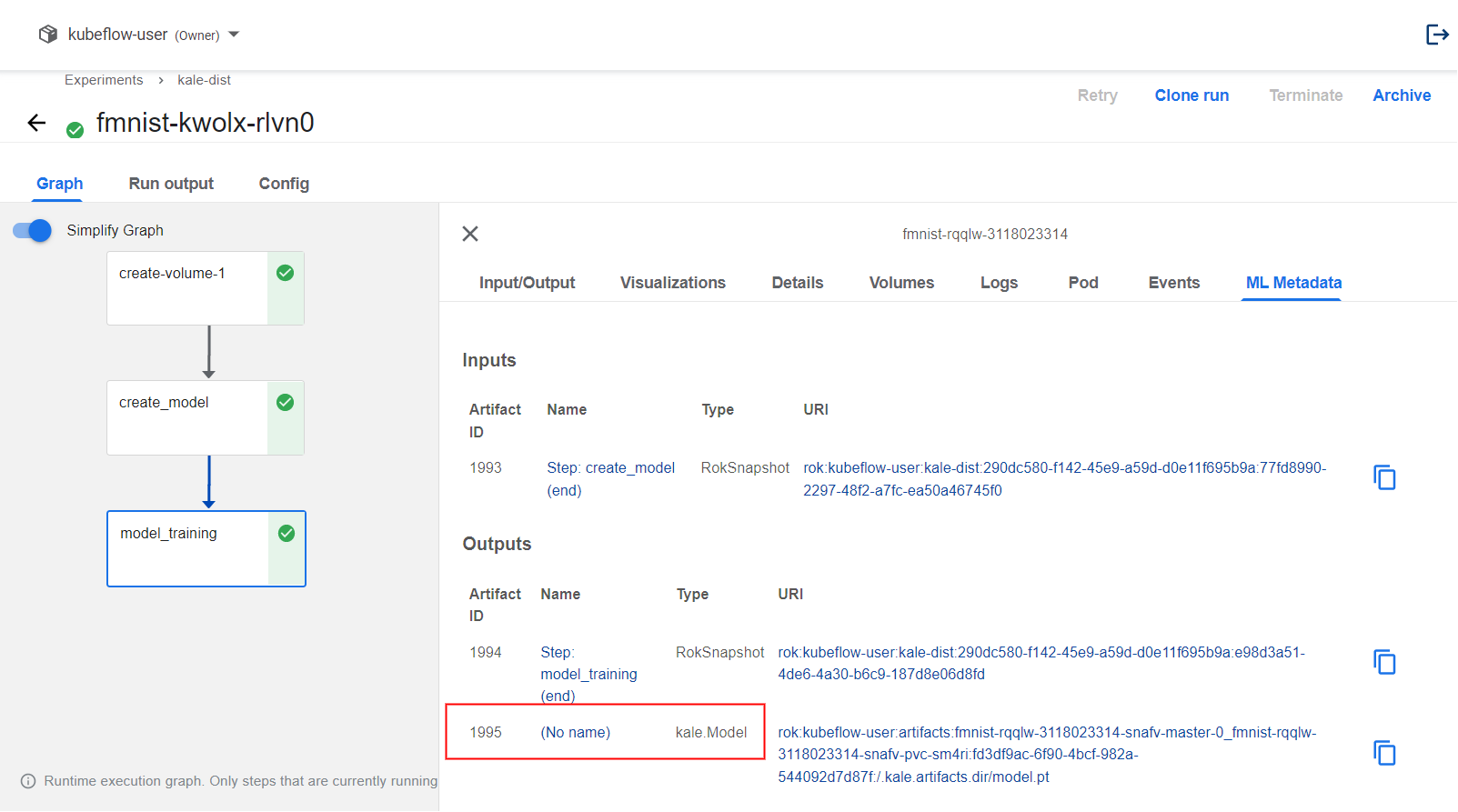
By clicking the
nameattribute of the artifact you can view the details of the model. These include general information about the model, such as its name, signature, computational graph, and the number of parameters, and other artifact metadata, such as tags, version, etc.: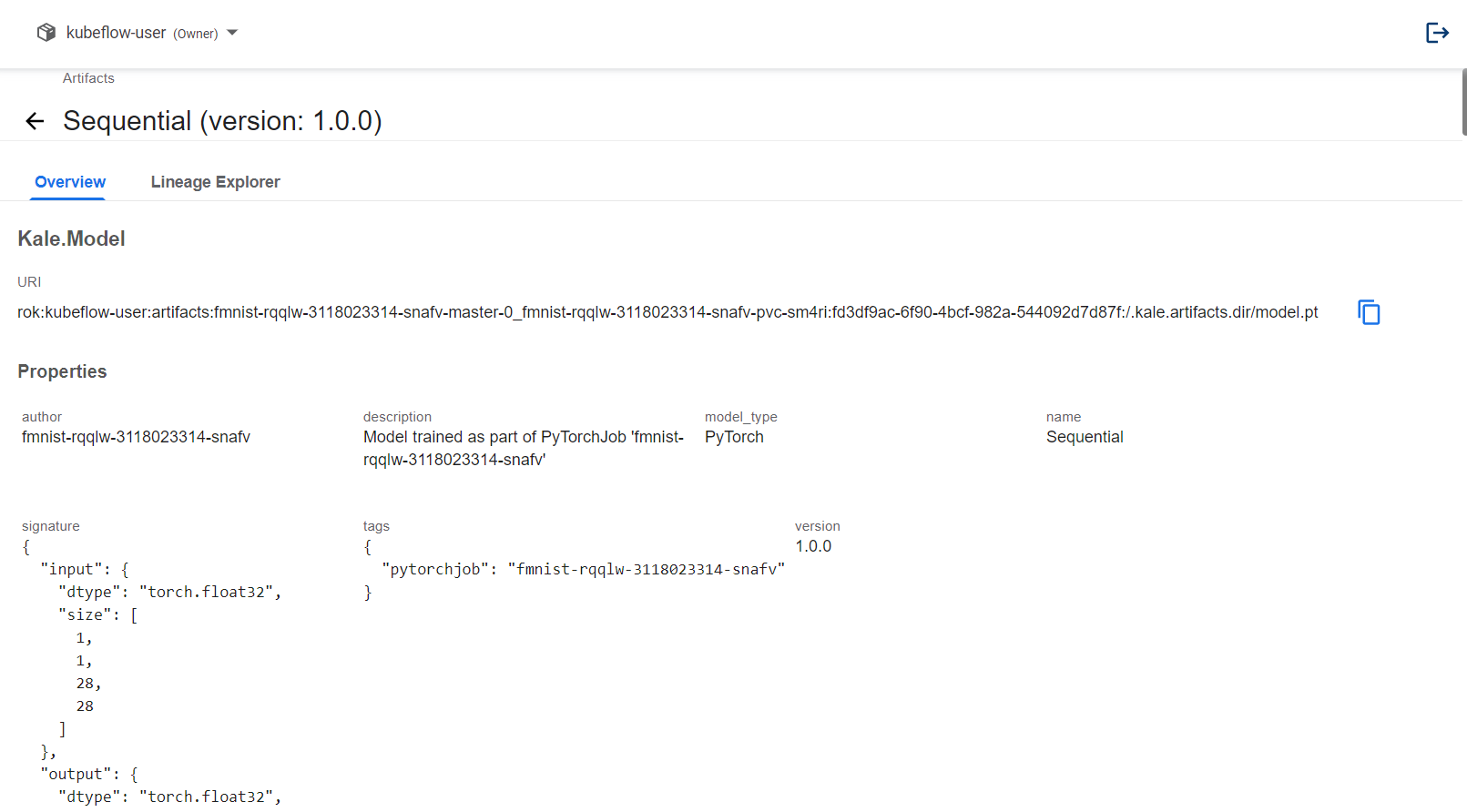
Summary¶
You have successfully created a pipeline with a step that runs a PyTorch distributed process, using Kale and the Kubeflow Training Operator.
What’s Next¶
The next step is to configure a PyTorch distributed KFP step using the Kale SDK.
