Serve Scikit Learn Models¶
This section will guide you through serving a Scikit Learn model, using the Kale
serve API.
Overview
What You’ll Need¶
- An Arrikto EKF or MiniKF deployment with the default Kale Docker image.
- An understanding of how the Kale SDK works.
- An understanding of how the Kale serve API works.
Procedure¶
This guide comprises three sections: In the first section, you will explore and process the dataset. Then, in the second section, you will leverage the Kale SDK to build a Machine Learning (ML) pipeline that trains and serves a Scikit Learn model. Finally, in the third section, you will invoke the model service to get predictions on a holdout test subset.
Explore Dataset¶
In this section, you will work with the 20newsgroups dataset. The
20newsgroups dataset consists of around 18000 newsgroups posts on
20 topics, split in two subsets: one for training and another one for
testing. The end goal is to classify each post into one of the 20 topics.
Create a new notebook server using the default Kale Docker image. The image will have the following naming scheme:
gcr.io/arrikto/jupyter-kale-py38:<IMAGE_TAG>Note
The
<IMAGE_TAG>varies based on the MiniKF or Arrikto EKF release.Connect to the server and create a new Jupyter notebook (that is, an IPYNB file):

Copy and paste the import statements in the first code cell, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:

In a different code cell, fetch the dataset and print the topic names. Copy and paste the following code, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:
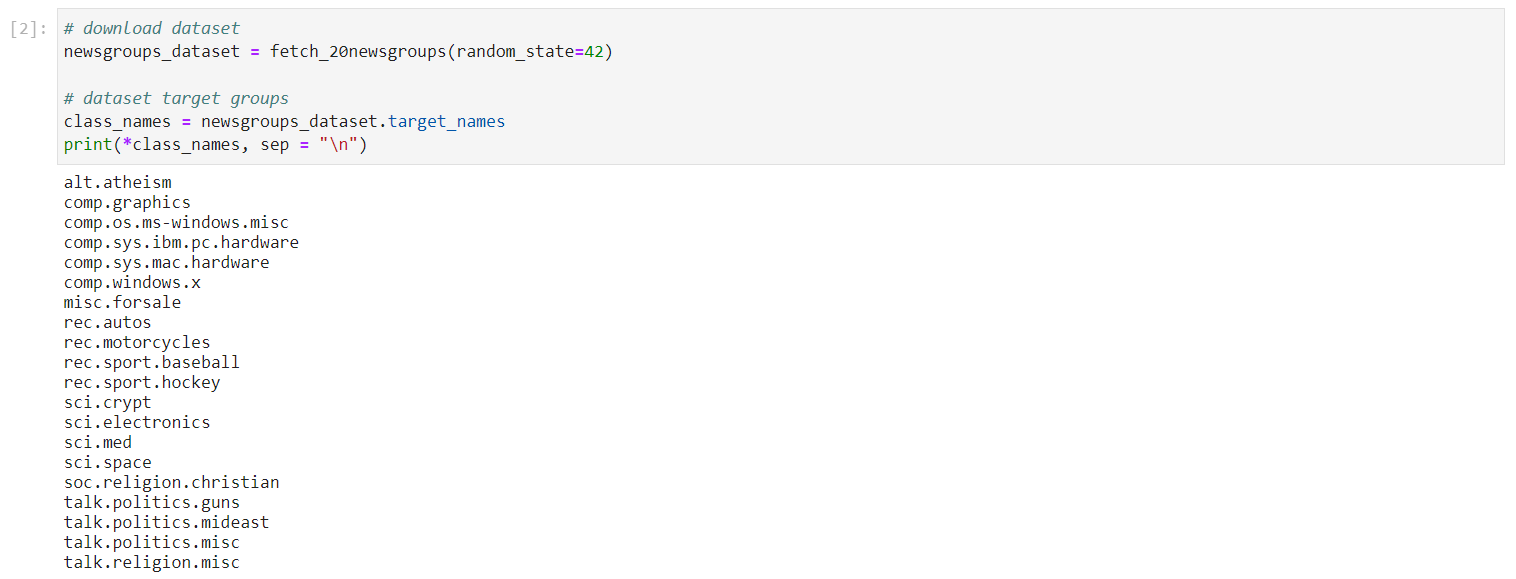
The output of the cell prints the 20 targets. You can see that posts in this dataset are classified into a diverse set of topics, including religion, politics, and sports.
Load the features and targets of the dataset, and split it into train and test subsets. In a new cell, copy and paste the following code, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:

Run the following code in a new cell to visualize an example from the training subset:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:
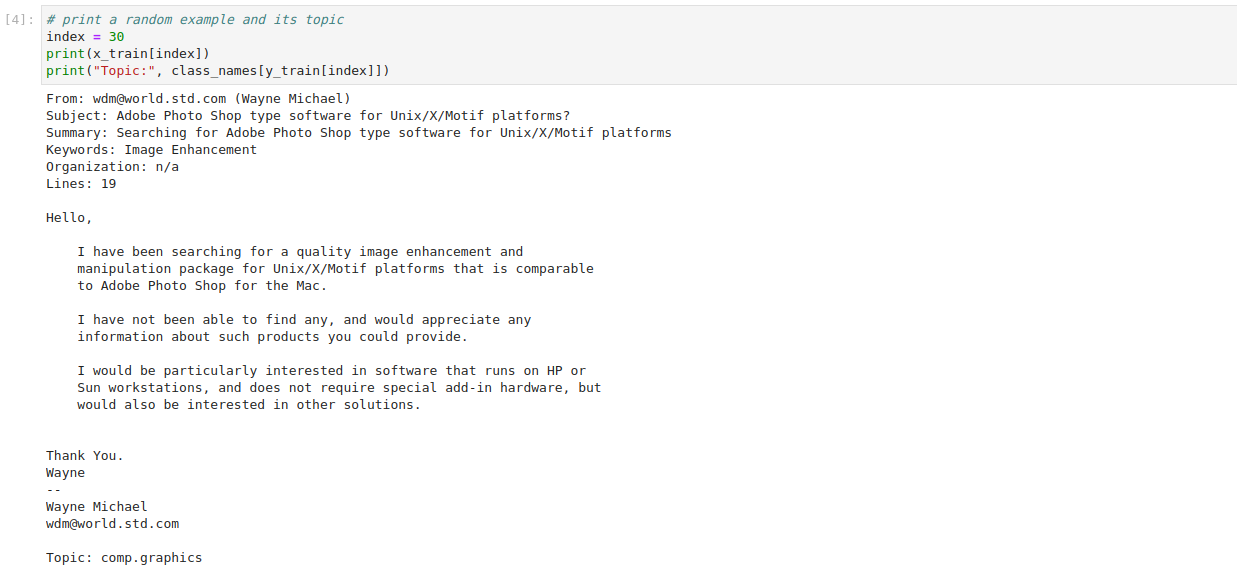
The output of the cell prints the text of a random example and its topic. You can see that the post asks a question about image enhancement and it is classified under the topic of
comp.graphics.Use the TF-IDF vectorizer to transform the raw training and test subsets into a form that you can use to train a machine learning model:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:

TF-IDF stands for Term Frequency - Inverse Document Frequency, and is a statistical term that evaluates the importance of a word within a document relative to a corpus. It computes the product of two terms:
- Term Frequency (TF): computes the frequency of words appearing in a document.
- Inverse Document Frequency (IDF): provides you with the importance of each word by weighting down the frequent words and scaling up the rare ones.
Serve Scikit Learn Model¶
In this section, you will build a pipeline that trains a Naive Bayes classifier to categorize the posts into different topics.
In the same notebook server, open a terminal, create a new Python file, and name it
serve_sklearn_model.py:$ touch serve_sklearn_model.pyCreate a new folder where you will place the transformer assets:
$ mkdir transformer_packageInside the
transformerfolder, create a new Python file, and name ittransformer.py:$ cd transformer_package && touch transformer.pyCopy and paste the following code inside
transformer.py:sklearn_transformer.py1 # Copyright © 2022 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 3 """Transformer. 4 5 This script defines a serving transformer which can preprocess raw data 6 and postprocess the predictions. 7 """ 8 9 import joblib 10 import kserve 11 12 from kale.serve import utils 13 from typing import Dict 14 15 16 class_names = ['alt.atheism', 'comp.graphics', 17 'comp.os.ms-windows.misc', 18 'comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware', 19 'comp.sys.mac.hardware', 20 'comp.windows.x', 'misc.forsale', 21 'rec.autos', 'rec.motorcycles', 22 'rec.sport.baseball', 'rec.sport.hockey', 23 'sci.crypt', 'sci.electronics', 'sci.med', 24 'sci.space', 'soc.religion.christian', 25 'talk.politics.guns', 'talk.politics.mideast', 26 'talk.politics.misc', 'talk.religion.misc'] 27 28 29 class Transformer(kserve.Model): 30 """Transform the data. 31 32 Vectorize the input data before passing it to the 33 model and return human-readable predictions. 34 35 Args: 36 name (str): The name of the Transformer 37 predictor_host (str): The host address of the Predictor 38 """ 39 40 def __init__(self, model_name: str, predictor_host: str, 41 protocol: str = "v1"): 42 super().__init__(model_name) 43 self.predictor_host = predictor_host 44 self.protocol = protocol 45 46 # load the vectorizer object 47 path = utils.get_transformer_asset("vectorizer.joblib") 48 with open(path, "rb") as f: 49 self.vectorizer = joblib.load(f) 50 51 def preprocess(self, inputs: Dict): 52 """Preprocess the dataset.""" 53 transformed_data = self.vectorizer.transform(inputs["instances"]) 54 return {'instances': transformed_data.toarray().tolist()} 55 56 def postprocess(self, inputs: Dict): 57 """Postprocess the predictions.""" 58 return {"predictions": [class_names[i] for i in inputs["predictions"]]} The
Transformerclass you defined extends thekserve.Modelclass, and overrides thepreprocessandpostprocessmethods.- KServe calls the
preprocessmethod before the server feeds the data to the model, to transform them in a form that the model understands. - KServe calls the
postprocessmethod on the model’s predictions, to return a human-readable result.
The
preprocessmethod has a global dependency: a TF-IDF vectorizer. To load this dependency, use theget_transformer_assetfunction, which knows how to find the file. More on this later, as you build the training pipeline.- KServe calls the
Return back to your home environment:
$ cdCopy and paste the following code inside
serve_sklearn_model.py:sklearn_starter.py1 # Copyright © 2022 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 3 """Kale SDK. 4 5 This script uses an ML pipeline to train and serve an SKLearn Model. 6 """ 7 8 import os 9 import joblib 10 11 from typing import Tuple, NamedTuple 12 13 from sklearn.feature_extraction import text 14 from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB 15 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups 16 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 17 from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer 18 19 from kale.types import MarshalData 20 from kale.sdk import pipeline, step 21 from kale.common import mlmdutils, artifacts 22 23 24 ASSETS_PATH = "/home/jovyan/transformer_package/" 25 26 27 @step(name="data_loading") 28 def load_split_dataset() -> Tuple[MarshalData, MarshalData]: 29 """Fetch 20newgroup dataset.""" 30 # load the data 31 newsgroups_dataset = fetch_20newsgroups(random_state=42) 32 x = newsgroups_dataset.data 33 y = newsgroups_dataset.target 34 35 x, _, y, _ = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=.2, random_state=42) 36 37 return x, y 38 39 40 @step(name="data_preprocess") 41 def preprocess(x: MarshalData) -> Tuple[MarshalData, int]: 42 """Preprocess the input data.""" 43 # get stopwords 44 stop_words = text.ENGLISH_STOP_WORDS 45 # TF-IDF vectors 46 vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=stop_words) 47 x_processed = vectorizer.fit_transform(x) 48 49 with open(os.path.join(ASSETS_PATH, "vectorizer.joblib"), "wb") as f: 50 joblib.dump(vectorizer, f) 51 52 # create and submit a Transformer artifact 53 mlmd = mlmdutils.get_mlmd_instance() 54 55 transformer_artifact = artifacts.Transformer( 56 name="Vectorizer", 57 transformer_dir=ASSETS_PATH, 58 module_name="transformer", 59 class_name="Transformer", 60 is_stateful=True 61 ).submit_artifact() 62 63 mlmd.link_artifact_as_output(transformer_artifact.id) 64 65 return x_processed, transformer_artifact.id 66 67 68 @step(name="model_training") 69 def train(x: MarshalData, 70 y: MarshalData) -> NamedTuple("outs", [("model", MarshalData)]): 71 """Train a MultinomialNB model.""" 72 classifier = MultinomialNB(alpha=.01) 73 model = classifier.fit(x, y) 74 return model 75 76 77 @pipeline(name="classification", experiment="sklearn-tutorial") 78 def ml_pipeline(): 79 """Run the ML pipeline.""" 80 x, y = load_split_dataset() 81 x_processed, _ = preprocess(x) 82 train(x_processed, y) 83 84 85 if __name__ == "__main__": 86 ml_pipeline() This script defines a KFP run using the Kale SDK. Specifically, it defines a pipeline with three steps:
- The first step (
data_loading) loads and splits the20newsgroupsdataset. - The second step (
data_preprocess) transforms the raw datasets using the TF-IDF vectorizer and creates aTransformerartifact. - The third step (
model_training) trains a Naive Bayes classifier.
Pay closer attention to the
preprocessstep. This step uses a TF-IDF vectorizer to transform the raw datasets into a form that the model can understand. Then, it saves thevectorizervariable inside thetransformer_packagefolder you created previously. Finally, it creates aTransformerartifact by passing the directory of the transformer assets, the name of the transformer module, and the name of the transformer class.Kale will
- move the
transformer_packagefolder to a location it controls (that’s how theget_transformer_assetfunction knows how to retrieve the assets), and - create and submit a
kale.Transformerartifact to MLMD.
- The first step (
Create a new step function which logs an
SKLearnModelartifact, using the Kale API. The following snippet summarizes the changes in code:Important
Running these pipelines locally won’t work. After introducing
register_modelstep, run the pipeline as a KFP pipeline since this step creates a Kubeflow artifact.sklearn_log_model_artifact.py1 # Copyright © 2022 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 3 """Kale SDK. 4-15 4 5 This script uses an ML pipeline to train and serve an SKLearn Model. 6 """ 7 8 import os 9 import joblib 10 11 from typing import Tuple, NamedTuple 12 13 from sklearn.feature_extraction import text 14 from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB 15 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups 16 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 17 from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer 18 19 + from kale.ml import Signature 20 from kale.types import MarshalData 21 from kale.sdk import pipeline, step 22 from kale.common import mlmdutils, artifacts 23-74 23 24 25 ASSETS_PATH = "/home/jovyan/transformer_package/" 26 27 28 @step(name="data_loading") 29 def load_split_dataset() -> Tuple[MarshalData, MarshalData]: 30 """Fetch 20newgroup dataset.""" 31 # load the data 32 newsgroups_dataset = fetch_20newsgroups(random_state=42) 33 x = newsgroups_dataset.data 34 y = newsgroups_dataset.target 35 36 x, _, y, _ = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=.2, random_state=42) 37 38 return x, y 39 40 41 @step(name="data_preprocess") 42 def preprocess(x: MarshalData) -> Tuple[MarshalData, int]: 43 """Preprocess the input data.""" 44 # get stopwords 45 stop_words = text.ENGLISH_STOP_WORDS 46 # TF-IDF vectors 47 vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=stop_words) 48 x_processed = vectorizer.fit_transform(x) 49 50 with open(os.path.join(ASSETS_PATH, "vectorizer.joblib"), "wb") as f: 51 joblib.dump(vectorizer, f) 52 53 # create and submit a Transformer artifact 54 mlmd = mlmdutils.get_mlmd_instance() 55 56 transformer_artifact = artifacts.Transformer( 57 name="Vectorizer", 58 transformer_dir=ASSETS_PATH, 59 module_name="transformer", 60 class_name="Transformer", 61 is_stateful=True 62 ).submit_artifact() 63 64 mlmd.link_artifact_as_output(transformer_artifact.id) 65 66 return x_processed, transformer_artifact.id 67 68 69 @step(name="model_training") 70 def train(x: MarshalData, 71 y: MarshalData) -> NamedTuple("outs", [("model", MarshalData)]): 72 """Train a MultinomialNB model.""" 73 classifier = MultinomialNB(alpha=.01) 74 model = classifier.fit(x, y) 75 return model 76 77 78 + @step(name="register_model") 79 + def register_model(model: MarshalData, x: MarshalData, y: MarshalData) -> int: 80 + mlmd = mlmdutils.get_mlmd_instance() 81 + 82 + signature = Signature( 83 + input_size=[1] + list(x[0].shape), 84 + output_size=[1] + list(y[0].shape), 85 + input_dtype=x.dtype, 86 + output_dtype=y.dtype) 87 + 88 + model_artifact = artifacts.SklearnModel( 89 + model=model, 90 + description="A simple MultinomialNB model", 91 + version="1.0.0", 92 + author="Kale", 93 + signature=signature, 94 + tags={"app": "sklearn-tutorial"}).submit_artifact() 95 + 96 + mlmd.link_artifact_as_output(model_artifact.id) 97 + return model_artifact.id 98 + 99 + 100 @pipeline(name="classification", experiment="sklearn-tutorial") 101 def ml_pipeline(): 102 """Run the ML pipeline.""" 103 x, y = load_split_dataset() 104 x_processed, _ = preprocess(x) 105 - train(x_processed, y) 106 + model = train(x_processed, y) 107 + register_model(model, x_processed, y) 108 109 110 if __name__ == "__main__": 111 ml_pipeline() Create a new step function which serves the
SKLearnModelartifact you created in the previous step, using the KaleserveAPI. The following snippet summarizes the changes in code:sklearn_serve.py1 # Copyright © 2022 Arrikto Inc. All Rights Reserved. 2 3 """Kale SDK. 4-15 4 5 This script uses an ML pipeline to train and serve an SKLearn Model. 6 """ 7 8 import os 9 import joblib 10 11 from typing import Tuple, NamedTuple 12 13 from sklearn.feature_extraction import text 14 from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB 15 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups 16 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 17 from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer 18 19 + from kale.serve import serve 20 from kale.ml import Signature 21 from kale.types import MarshalData 22 from kale.sdk import pipeline, step 23-97 23 from kale.common import mlmdutils, artifacts 24 25 26 ASSETS_PATH = "/home/jovyan/transformer_package/" 27 28 29 @step(name="data_loading") 30 def load_split_dataset() -> Tuple[MarshalData, MarshalData]: 31 """Fetch 20newgroup dataset.""" 32 # load the data 33 newsgroups_dataset = fetch_20newsgroups(random_state=42) 34 x = newsgroups_dataset.data 35 y = newsgroups_dataset.target 36 37 x, _, y, _ = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=.2, random_state=42) 38 39 return x, y 40 41 42 @step(name="data_preprocess") 43 def preprocess(x: MarshalData) -> Tuple[MarshalData, int]: 44 """Preprocess the input data.""" 45 # get stopwords 46 stop_words = text.ENGLISH_STOP_WORDS 47 # TF-IDF vectors 48 vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=stop_words) 49 x_processed = vectorizer.fit_transform(x) 50 51 with open(os.path.join(ASSETS_PATH, "vectorizer.joblib"), "wb") as f: 52 joblib.dump(vectorizer, f) 53 54 # create and submit a Transformer artifact 55 mlmd = mlmdutils.get_mlmd_instance() 56 57 transformer_artifact = artifacts.Transformer( 58 name="Vectorizer", 59 transformer_dir=ASSETS_PATH, 60 module_name="transformer", 61 class_name="Transformer", 62 is_stateful=True 63 ).submit_artifact() 64 65 mlmd.link_artifact_as_output(transformer_artifact.id) 66 67 return x_processed, transformer_artifact.id 68 69 70 @step(name="model_training") 71 def train(x: MarshalData, 72 y: MarshalData) -> NamedTuple("outs", [("model", MarshalData)]): 73 """Train a MultinomialNB model.""" 74 classifier = MultinomialNB(alpha=.01) 75 model = classifier.fit(x, y) 76 return model 77 78 79 @step(name="register_model") 80 def register_model(model: MarshalData, x: MarshalData, y: MarshalData) -> int: 81 mlmd = mlmdutils.get_mlmd_instance() 82 83 signature = Signature( 84 input_size=[1] + list(x[0].shape), 85 output_size=[1] + list(y[0].shape), 86 input_dtype=x.dtype, 87 output_dtype=y.dtype) 88 89 model_artifact = artifacts.SklearnModel( 90 model=model, 91 description="A simple MultinomialNB model", 92 version="1.0.0", 93 author="Kale", 94 signature=signature, 95 tags={"app": "sklearn-tutorial"}).submit_artifact() 96 97 mlmd.link_artifact_as_output(model_artifact.id) 98 return model_artifact.id 99 100 101 + @step(name="serve_model") 102 + def serve_model(model_artifact_id: int, transformer_artifact_id: int): 103 + serve_config = {"limits": {"memory": "4Gi"}, 104 + "annotations": {"sidecar.istio.io/inject": "false"}} 105 + serve(name="sklearn-tutorial", 106 + model_id=model_artifact_id, 107 + transformer_id=transformer_artifact_id, 108 + serve_config=serve_config) 109 + 110 + 111 @pipeline(name="classification", experiment="sklearn-tutorial") 112 def ml_pipeline(): 113 """Run the ML pipeline.""" 114 x, y = load_split_dataset() 115 - x_processed, _ = preprocess(x) 116 + x_processed, transformer_artifact_id = preprocess(x) 117 model = train(x_processed, y) 118 - register_model(model, x_processed, y) 119 + artifact_id = register_model(model, x_processed, y) 120 + serve_model(artifact_id, transformer_artifact_id) 121 122 123 if __name__ == "__main__": 124 ml_pipeline() Deploy and run your code as a KFP pipeline:
$ python3 -m kale serve_sklearn_model.py --kfpSelect Runs to view the KFP run you just created. This is what it looks like when the pipeline completes successfully:
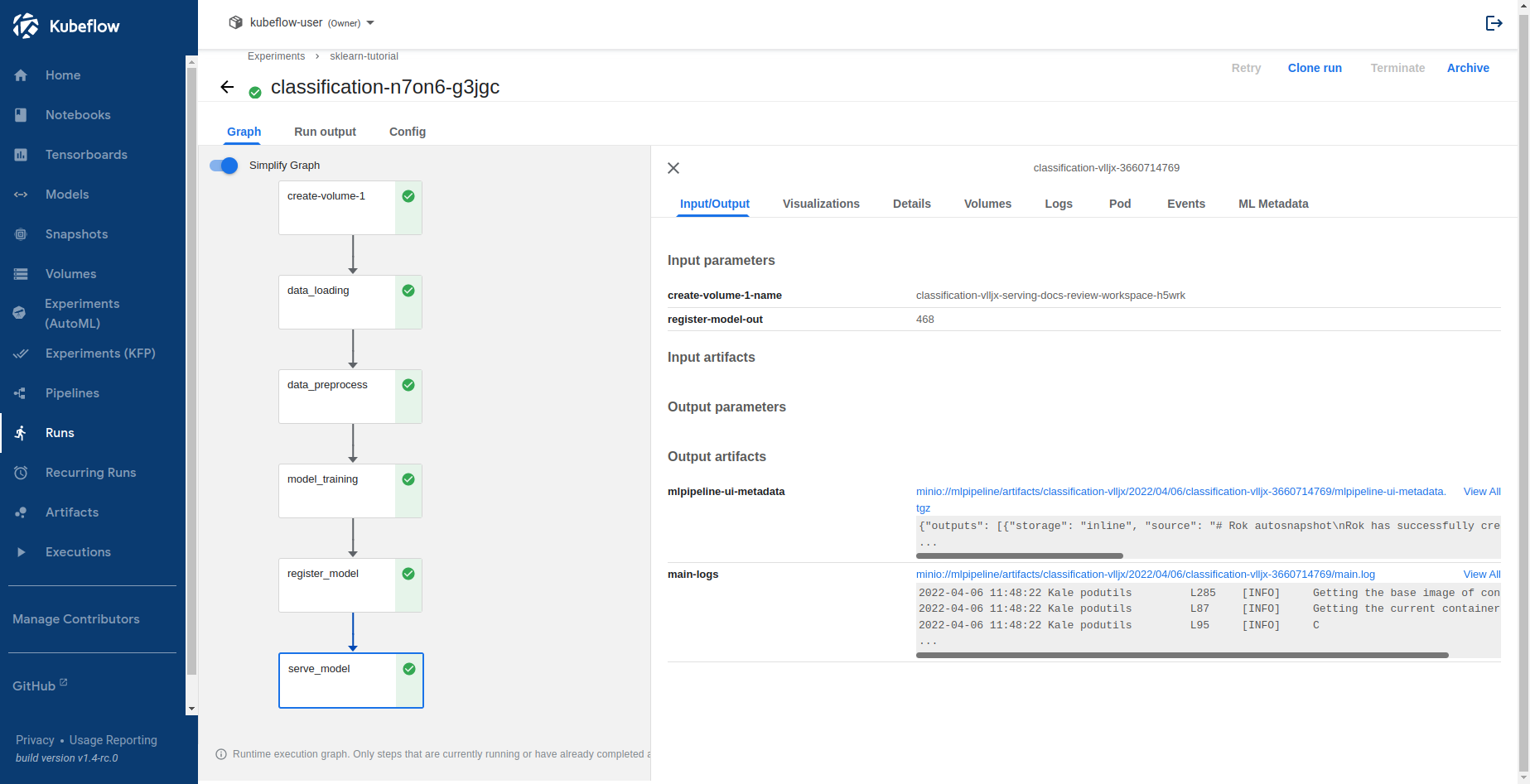
When the
register_modelstep completes, you can view the model artifact through the KFP UI: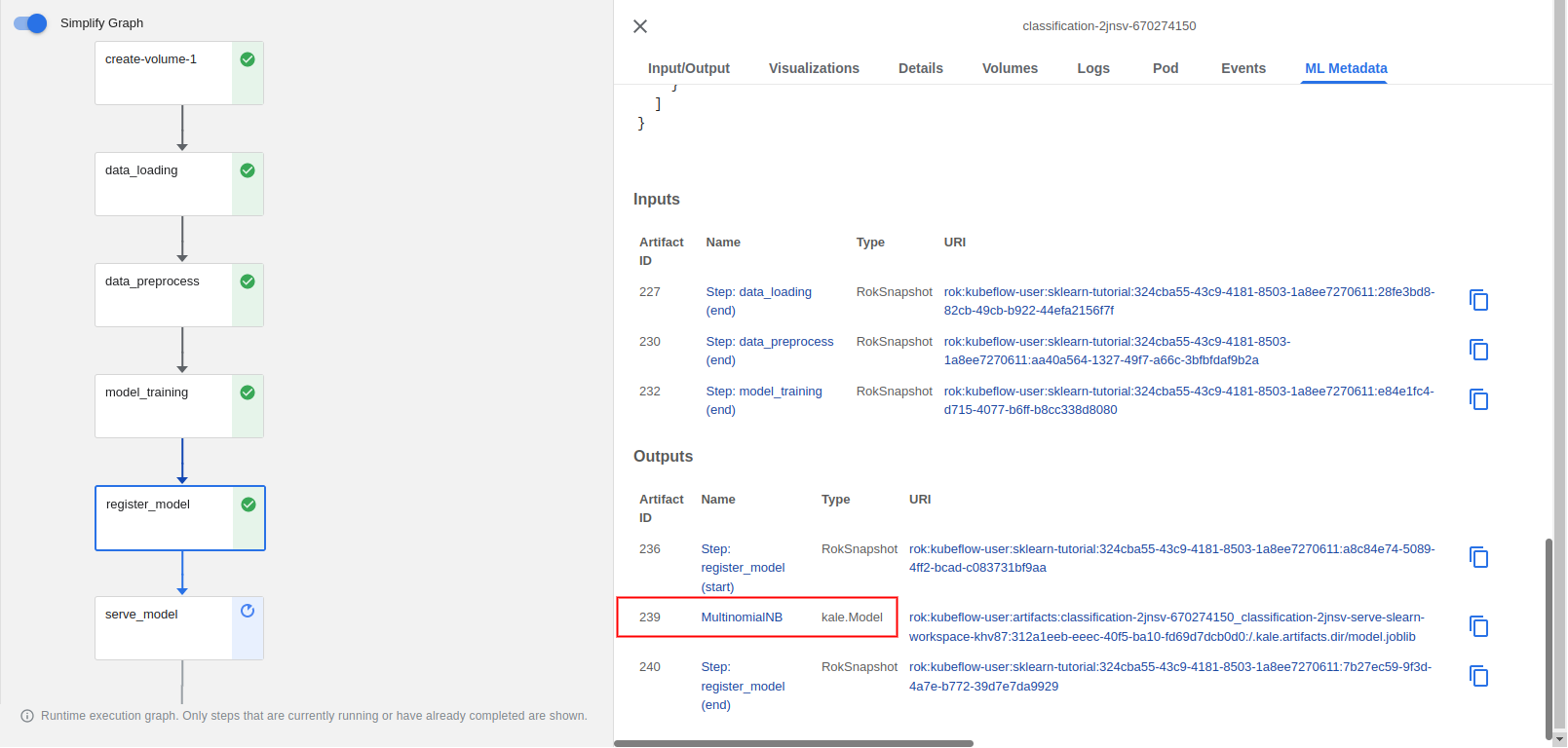
Wait until the pipeline completes. Check the Logs tab of the
serve_modelstep to see whether theInferenceServiceis running.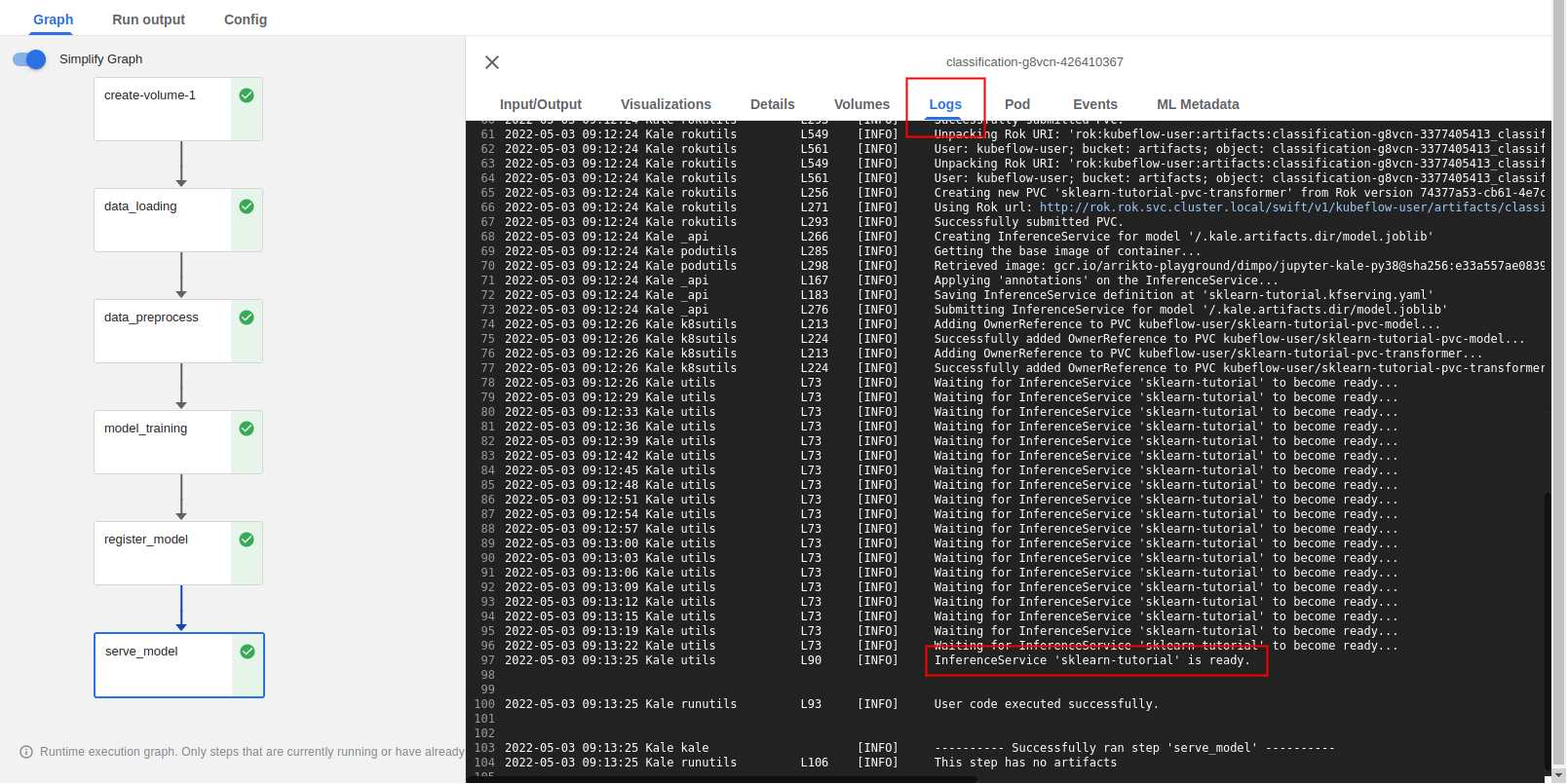
Select Models and click on the endpoint you created:
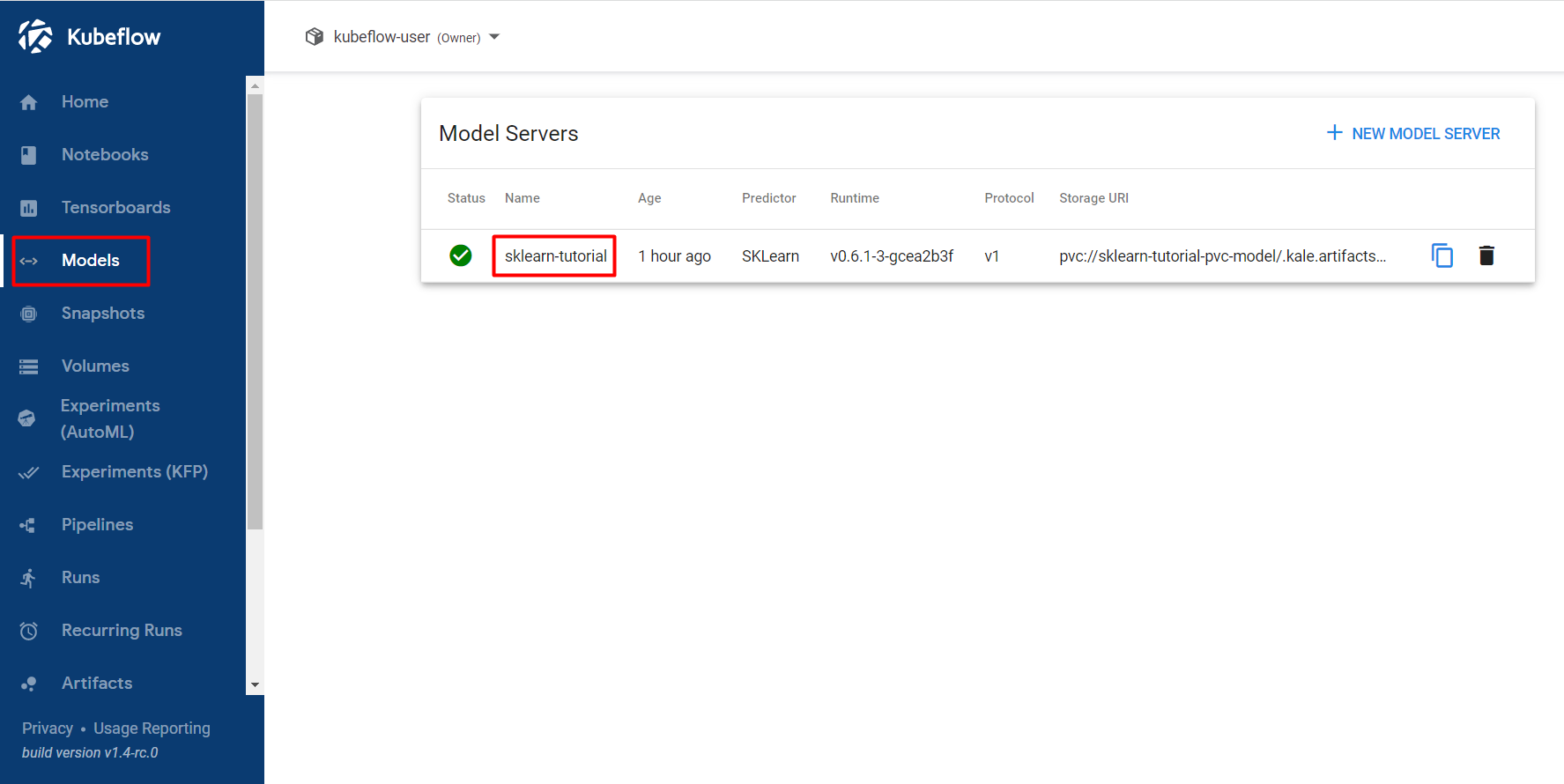
Get Predictions¶
In this section, you will query the model endpoint to get predictions for the posts in the test subset.
Navigate to the Models UI to retrieve the name of the
InferenceService. In this example, it issklearn-tutorial.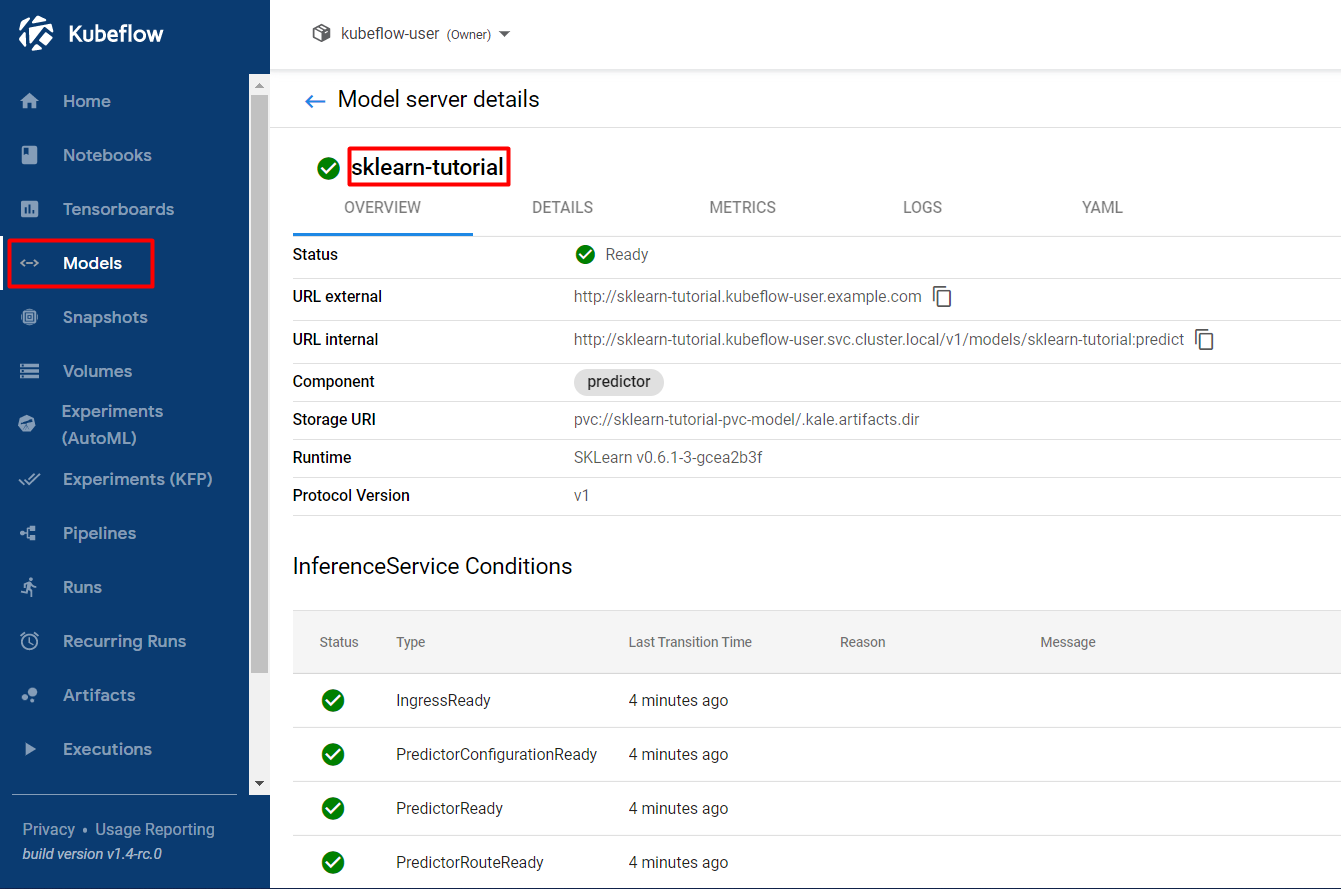
In the existing notebook, in a different code cell, initialize a Kale
Endpointobject using the name of theInferenceServiceyou retrieved in the previous step. Then, run the cell:Note
When initializing an
Endpoint, you can also pass the namespace of theInferenceService. For example, if your namespace ismy-namespace:If you do not provide one, Kale assumes the namespace of the notebook server. In our case it is
kubeflow-user.This is how your notebook cell will look like:

Visualize a test sample and transform the data into JSON format. Copy and paste the following code in a new cell, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:
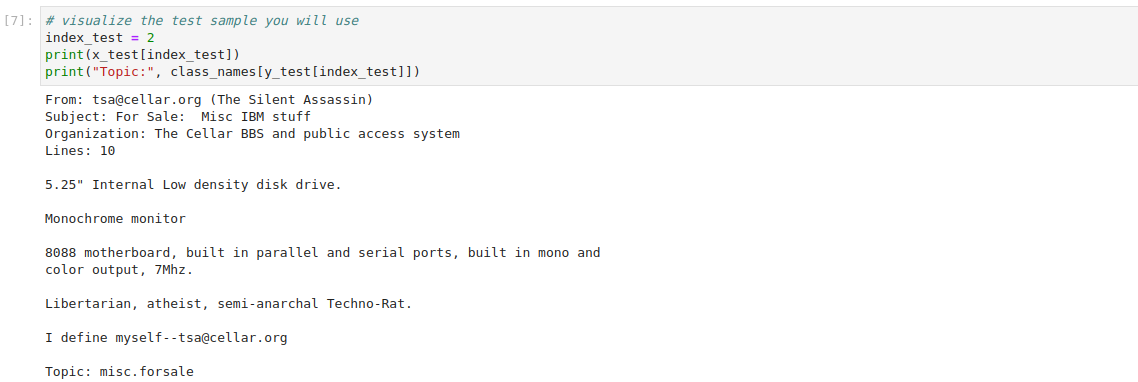
Prepare the data payload for the prediction request. Copy and paste the following code in a new cell, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:
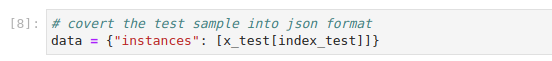
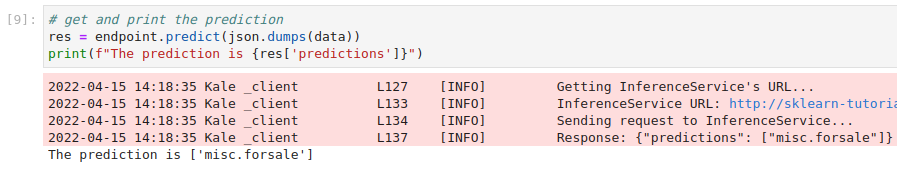
Invoke the server to get predictions. Copy and paste the following snippet in a different code cell, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like: