Use Arrikto vGPUs¶
Currently, Kubernetes assigns GPUs exclusively to Pods. This is especially inefficient in interactive scenarios, such as development using a Jupyter notebook server, in which a Pod, or application, has large idle periods.
Kiwi is a mechanism that enables multiple containers (belonging to the same or different Pods) to run on the same GPU concurrently, each one having the whole GPU memory available for use.
This section will guide you through using vGPUs for your workloads. Here is what you’ll need to follow this guide:
- An existing Kiwi deployment on your Kubernetes cluster.
Overview
Use Arrikto vGPU for Kubernetes Workload¶
In order to consume an Arrikto vGPU, you need to request exactly one
arrikto.com/gpu device in the limits section of the resources
of your container. To do this, add the following snippet to the desired
container’s spec:
Create Arrikto vGPU-enabled Jupyter Notebook Server¶
When creating a Jupyter notebook server, specify exactly one
arrikto.com/gpu in the GPUs section of the Jupyter Web App.
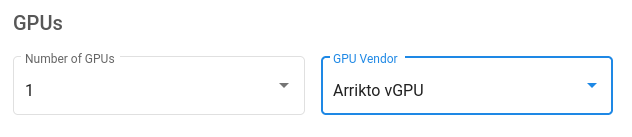
Additionally, make sure to use a GPU-enabled Kale image, as you would normally do for your GPU-enabled notebook.
See also
Use Arrikto vGPU in Kale Notebook Cell¶
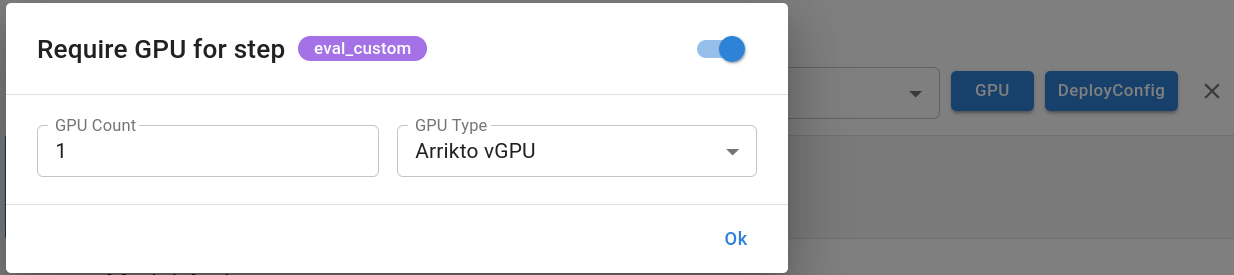
Specify exactly one Arrikto vGPU in the GPU-specific annotation modal that appears after clicking the GPU button when annotating a step.
See also
