Gather Logs for Troubleshooting¶
This section describes how to gather any EKF-related logs in order to troubleshoot your deployment. At the end of this guide you will end up with a tarball that you can send to the Arrikto Support Team.
Choose one of the following options to gather logs for troubleshooting:
Overview
What You'll Need¶
- A configured management environment.
- An existing Kubernetes cluster.
- An existing Rok deployment.
- An existing Kubeflow deployment.
Option 1: Gather Logs Automatically (preferred)¶
Gather logs by following the on-screen instructions on the rok-gather-logs
user interface.
Start the
rok-gather-logsCLI tool:root@rok-tools:~# rok-gather-logs
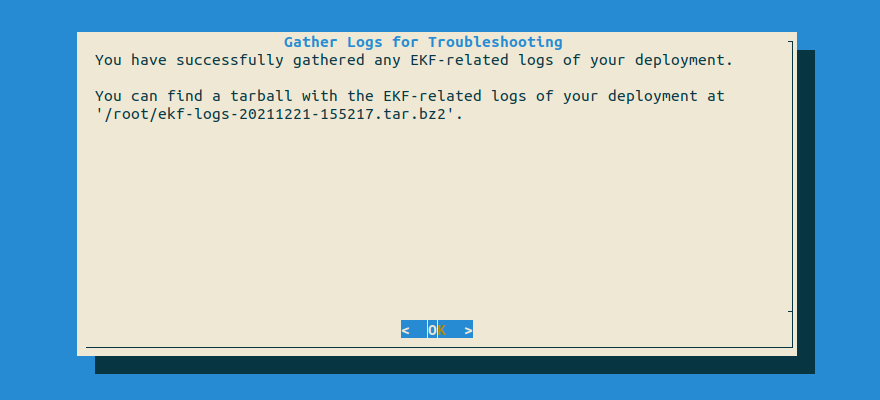
Wait until the script has finished successfully.
Troubleshooting
The script reports timeout errors
Inspect the last lines of
~/.rok/log/gather-logs.log. If they report a warning message similar to this:socket.timeout: timed out ... urllib3.exceptions.ConnectTimeoutError: (<urllib3.connection.VerifiedHTTPSConnection object at 0x7fbd39c60d30>, 'Connection to 0b15546e6290295416ca651a36d6b692.gr7.eu-central-1.eks.amazonaws.com timed out. (connect timeout=1.0)') ... urllib3.exceptions.MaxRetryError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='0b15546e6290295416ca651a36d6b692.gr7.eu-central-1.eks.amazonaws.com', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /api/v1/nodes?labelSelector= (Caused by ConnectTimeoutError(<urllib3.connection.VerifiedHTTPSConnection object at 0x7fbd39c60d30>, 'Connection to 0b15546e6290295416ca651a36d6b692.gr7.eu-central-1.eks.amazonaws.com timed out. (connect timeout=1.0)'))
it means that the Kubernetes API server takes a while to respond. Change the timeouts accordingly and rerun the script. If you want to give the server more time to respond, try increasing the timeouts. For example:
root@rok-tools:~# rok-gather-logs \ > --connection-timeout "2 minutes" \ > --read-timeout "10 minutes"
The script reported warnings
If the above command reports a warning message similar to this:
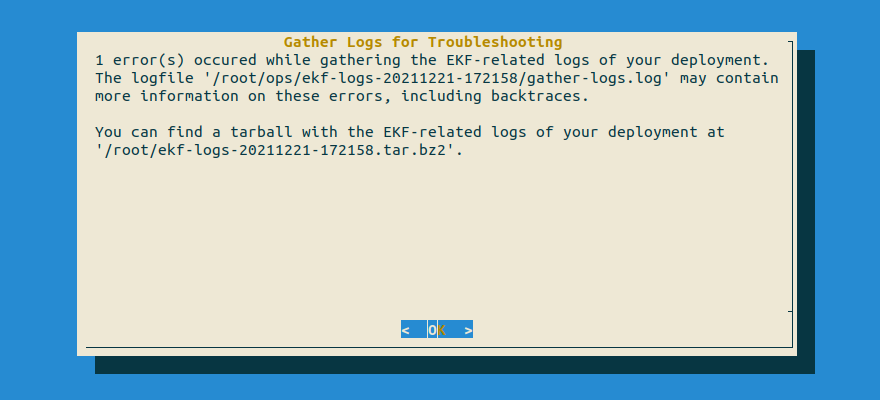
it means that some of the steps in the log gathering process couldn't complete successfully, probably due to a degraded cluster.
Proceed with the tarball that
rok-gather-logsproduced, as it reports the steps that have failed and the reason for their failure. To see which steps have failed for yourself, inspect the file(s) thatrok-gather-logsreports.The script crashed
If the above command crashes with an error, please report it to the Arrikto Support Team.
Contact Arrikto
Open the logs under
~/.rok/log/gather-logs.log, go to the end of the file, and send us the lines that show an error.Find the tarball under
$HOME. Copy the output to your clipboard, as you are going to use it later:root@rok-tools:~# export TARBALL=$(ls -t ~/*tar.gz | head -1) && echo ${TARBALL?} /root/ekf-logs-20211221-155217.tar.gz
Proceed to the Summary section.
Option 2: Gather Logs Manually¶
If you want to gather logs manually, follow the instructions below.
Procedure¶
Switch to your management environment.
Get the current timestamp:
root@rok-tools:~# export TIMESTAMP=$(date +%Y%m%d-%H%M%S)
Use the timestamp to specify a name for the logs directory:
root@rok-tools:~# export NAME=ekf-logs-${TIMESTAMP?}
Set the working directory:
root@rok-tools:~# export WORKDIR=~/ops
Note
You may also store any files under
$HOMEso that everything is persistent and easily accessible.Set the directory to use for saving the logs:
root@rok-tools:~# export LOGDIR=$(realpath ${WORKDIR?}/${NAME?})
Create the directory and enter it:
root@rok-tools:~# mkdir -p ${LOGDIR?} && cd ${LOGDIR?}
Get Kubernetes nodes:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get nodes -o wide > nodes.txt
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get nodes -o yaml > nodes.yaml
Get Pods in all namespaces:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -A -o wide > pods.txt
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -A -o yaml > pods.yaml
Get events in all namespaces:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get events --sort-by=.lastTimestamp -A -o wide > events.txt
Get RokCluster status:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get rokcluster -n rok rok > rokcluster.txt
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get rokcluster -n rok rok -o yaml > rokcluster.yaml
Get Pods in the
rok-systemnamespace:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -n rok-system -o wide > rok-system-pods.txt
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -n rok-system -o yaml > rok-system-pods.yaml
Get the logs of all Pods in the
rok-systemnamespace:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods \ > -n rok-system \ > -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name --no-headers \ > | while read pod; do > kubectl logs -n rok-system ${pod} --all-containers > ${pod}.log > done
Get Pods in the
roknamespace:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -n rok -o wide > rok-pods.txt
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -n rok -o yaml > rok-pods.yaml
Get the logs of all Pods in the
roknamespace:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods \ > -n rok \ > -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name --no-headers \ > | while read pod; do > kubectl logs -n rok ${pod} --all-containers > ${pod}.log > done
Find the master Rok Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -l role=master,app=rok -n rok -o wide > rok-master.txt
Get the logs of the master Rok Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl logs -n rok svc/rok --all-containers > rok-master.log
Troubleshooting
kubectl hangs
This means that the service has no endpoints because the RokCluster has problems with master election. Press Ctrl-C to interrupt the command and proceed with the next steps.
Get the logs of all Rok Pods:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods \ > -n rok \ > -l app=rok \ > -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name --no-headers \ > | while read pod; do > kubectl cp rok/${pod}:/var/log/rok ${pod}-var-log-rok > done
Get RokCluster members:
Get the configured members of the cluster:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl exec \ > -ti -n rok ds/rok \ > -- bash \ > -i -c "rok-cluster member-list" > rok-cluster-member-list.txt
Get the runtime members of the cluster:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl exec \ > -ti -n rok ds/rok \ > -- bash \ > -i -c "rok-election-ctl member-list" > rok-election-ctl-member-list.txt
Get Rok locks:
Get the composition-related locks:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl exec \ > -ti -n rok ds/rok \ > -- bash \ > -i -c "rok-dlm --etcd-endpoint http://rok-etcd.rok.svc.cluster.local:2379 --dlm-namespace composer lock-list" > rok-dlm-locks-composer.txt
Get the election-related locks:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl exec \ > -ti -n rok ds/rok \ > -- bash \ > -i -c "rok-dlm --etcd-endpoint http://rok-etcd.rok.svc.cluster.local:2379 --dlm-namespace election lock-list" > rok-dlm-locks-election.txt
Get PVCs of all namespaces:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pvc -A > pvc.txt
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pvc -A -o yaml > pvc.yaml
Get PVs:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pv > pv.txt
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pv -o yaml > pv.yaml
Inspect Rok local storage on all nodes:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods \ > -n rok-system \ > -l name=rok-disk-manager \ > -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,NODE:.spec.nodeName --no-headers \ > | while read rdm node; do > kubectl exec -n rok-system ${rdm} -- vgs > ${node}-vgs.txt > kubectl exec -n rok-system ${rdm} -- df -h /mnt/data/rok > ${node}-df.txt > done
Get the logs of the Dex Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get svc -n auth dex &> /dev/null && \ > kubectl logs -n auth svc/dex --all-containers > dex.log
Get the logs of the AuthService Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl logs -n istio-system svc/authservice --all-containers > authservice.log
Get the logs of the Reception Server Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl logs -n kubeflow svc/kubeflow-reception --all-containers > kubeflow-reception.log
Get the logs of the Profile Controller Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl logs -n kubeflow svc/profiles-kfam --all-containers > profiles-kfam.log
Set the tarball name:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# export TARBALL=$(realpath ~/${NAME}.tar.gz)
Create tarball:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# env GZIP=-1 tar -C ${WORKDIR?} -czvf ${TARBALL?} ${NAME?}
Find the tarball under
$HOME. Copy the output to your clipboard, as you are going to use it later:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# cd && echo ${TARBALL?} /root/ekf-logs-20211221-155217.tar.gz
What's Next¶
The next step is to send the tarball to the Arrikto Support Team.
