Gather Logs for Troubleshooting¶
This section describes how to gather any EKF-related logs in order to troubleshoot your deployment. At the end of this guide you will end up with a tarball that you can send to the Arrikto Support Team.
Choose one of the following options to gather logs for troubleshooting:
Overview
What You’ll Need¶
- A configured management environment.
- An existing Kubernetes cluster.
- An existing Rok deployment.
- An existing Kubeflow deployment.
Option 1: Gather Logs Automatically (preferred)¶
Gather logs by following the on-screen instructions on the rok-gather-logs
user interface.
Start the
rok-gather-logsCLI tool:root@rok-tools:~# rok-gather-logs
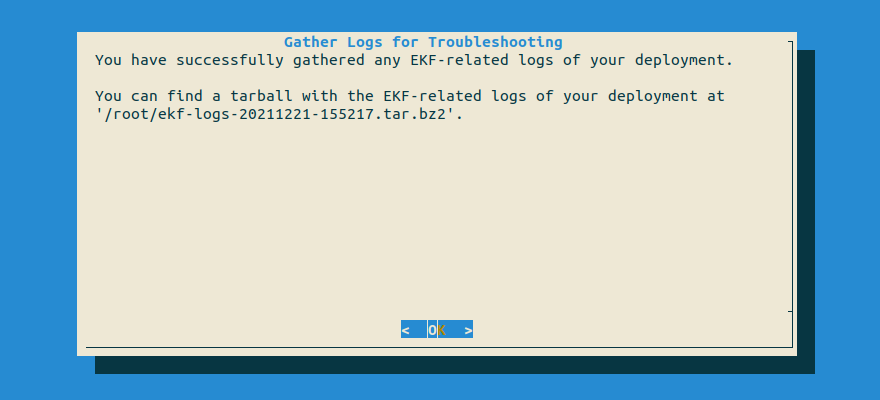
Wait until the script has finished successfully.
Troubleshooting
The script takes too long to complete and/or runs out of space
If the script takes too long to complete and/or runs out of space, you can do the following:
Press
Ctrl+Cto stop the script.Start the
rok-gather-logstool again:root@rok-tools:~# rok-gather-logs(Optional) When prompted, select a smaller limit for the size of the logs of the Rok and Rok CLI Node Pods that the tool will gather from each node of your cluster. The recommended value is
100 MiB.(Optional) When prompted, select a subset of the cluster nodes to gather logs from, if you have pinpointed the problematic nodes of your cluster.
The script reports timeout errors
Inspect the last lines of
~/.rok/log/gather-logs.log. If they report a warning message similar to this:socket.timeout: timed out ... urllib3.exceptions.ConnectTimeoutError: (<urllib3.connection.VerifiedHTTPSConnection object at 0x7fbd39c60d30>, 'Connection to 0b15546e6290295416ca651a36d6b692.gr7.eu-central-1.eks.amazonaws.com timed out. (connect timeout=1.0)') ... urllib3.exceptions.MaxRetryError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='0b15546e6290295416ca651a36d6b692.gr7.eu-central-1.eks.amazonaws.com', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /api/v1/nodes?labelSelector= (Caused by ConnectTimeoutError(<urllib3.connection.VerifiedHTTPSConnection object at 0x7fbd39c60d30>, 'Connection to 0b15546e6290295416ca651a36d6b692.gr7.eu-central-1.eks.amazonaws.com timed out. (connect timeout=1.0)'))it means that the Kubernetes API server takes a while to respond. Change the timeouts accordingly and rerun the script. If you want to give the server more time to respond, try increasing the timeouts. For example:
root@rok-tools:~# rok-gather-logs \ > --connection-timeout "2 minutes" \ > --read-timeout "10 minutes"The script reported warnings
If the above command reports a warning message similar to this:
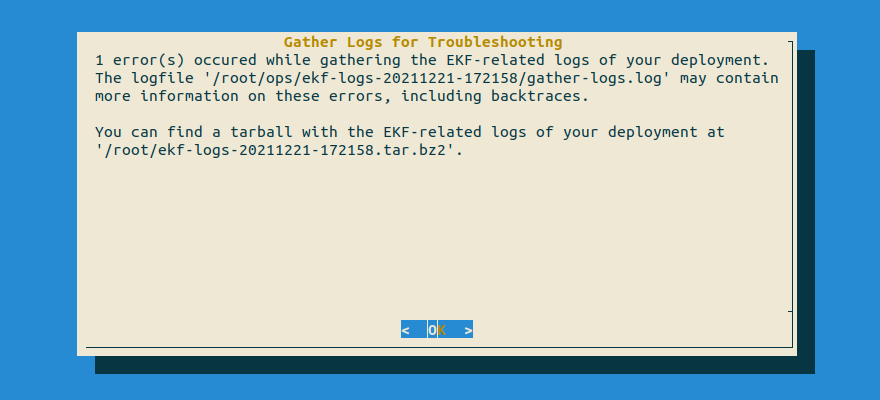
it means that some of the steps in the log gathering process couldn’t complete successfully, probably due to a degraded cluster.
Proceed with the tarball that
rok-gather-logsproduced, as it reports the steps that have failed and the reason for their failure. To see which steps have failed for yourself, inspect the file(s) thatrok-gather-logsreports.The script crashed
If the above command crashes with an error, please report it to the Arrikto Support Team.
Contact Arrikto
Open the logs under
~/.rok/log/gather-logs.log, go to the end of the file, and send us the lines that show an error.Find the tarball under
$HOME. Copy the output to your clipboard, as you are going to use it later:root@rok-tools:~# export TARBALL=$(ls -t ~/*tar.gz | head -1) && echo ${TARBALL?} /root/ekf-logs-20211221-155217.tar.gz
Proceed to the Summary section.
Option 2: Gather Logs Manually¶
If you want to gather logs manually, follow the instructions below.
Note
The manual instructions do not support limiting the size of the logs or selecting specific nodes to gather logs from. If you need these options, follow Option 1: Gather Logs Automatically (preferred).
Procedure¶
Switch to your management environment.
Get the current timestamp:
root@rok-tools:~# export TIMESTAMP=$(date +%Y%m%d-%H%M%S)Use the timestamp to specify a name for the logs directory:
root@rok-tools:~# export NAME=ekf-logs-${TIMESTAMP?}Set the working directory:
root@rok-tools:~# export WORKDIR=~/opsNote
You may also store any files under
$HOMEso that everything is persistent and easily accessible.Set the directory to use for saving the logs:
root@rok-tools:~# export LOGDIR=$(realpath ${WORKDIR?}/${NAME?})Create the directory and enter it:
root@rok-tools:~# mkdir -p ${LOGDIR?} && cd ${LOGDIR?}Get Kubernetes nodes:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get nodes -o wide > nodes.txtroot@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get nodes -o yaml > nodes.yamlGet Pods in all namespaces:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -A -o wide > pods.txtroot@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -A -o yaml > pods.yamlGet events in all namespaces:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get events --sort-by=.lastTimestamp -A -o wide > events.txtGet RokCluster status:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get rokcluster -n rok rok > rokcluster.txtroot@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get rokcluster -n rok rok -o yaml > rokcluster.yamlGet Pods in the
rok-systemnamespace:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -n rok-system -o wide > rok-system-pods.txtroot@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -n rok-system -o yaml > rok-system-pods.yamlGet the logs of all Pods in the
rok-systemnamespace:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods \ > -n rok-system \ > -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name --no-headers \ > | while read pod; do > kubectl logs -n rok-system ${pod} --all-containers > ${pod}.log > doneGet Pods in the
roknamespace:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -n rok -o wide > rok-pods.txtroot@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -n rok -o yaml > rok-pods.yamlGet the logs of all Pods in the
roknamespace:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods \ > -n rok \ > -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name --no-headers \ > | while read pod; do > kubectl logs -n rok ${pod} --all-containers > ${pod}.log > doneFind the master Rok Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods -l role=master,app=rok -n rok -o wide > rok-master.txtGet the logs of the master Rok Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl logs -n rok svc/rok --all-containers > rok-master.logTroubleshooting
kubectl hangs
This means that the service has no endpoints because the RokCluster has problems with master election. Press
Ctrl+Cto interrupt the command and proceed with the next steps.Get the logs of all Rok Pods:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods \ > -n rok \ > -l app=rok \ > -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name --no-headers \ > | while read pod; do > kubectl cp rok/${pod}:/var/log/rok ${pod}-var-log-rok > kubectl cp rok/${pod}:/root/.rok/log ${pod}-root-rok-log > doneGet RokCluster members:
Get the configured members of the cluster:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl exec \ > -ti -n rok ds/rok \ > -- bash \ > -i -c "rok-cluster member-list" > rok-cluster-member-list.txtGet the runtime members of the cluster:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl exec \ > -ti -n rok ds/rok \ > -- bash \ > -i -c "rok-election-ctl member-list" > rok-election-ctl-member-list.txt
Get Rok locks:
Get the composition-related locks:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl exec \ > -ti -n rok ds/rok \ > -- bash \ > -i -c "rok-dlm --etcd-endpoint http://rok-etcd.rok.svc.cluster.local:2379 --dlm-namespace composer lock-list" > rok-dlm-locks-composer.txtGet the election-related locks:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl exec \ > -ti -n rok ds/rok \ > -- bash \ > -i -c "rok-dlm --etcd-endpoint http://rok-etcd.rok.svc.cluster.local:2379 --dlm-namespace election lock-list" > rok-dlm-locks-election.txt
Get PVCs in all namespaces:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pvc -A > pvc.txtroot@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pvc -A -o yaml > pvc.yamlGet PVs:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pv > pv.txtroot@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pv -o yaml > pv.yamlInspect Rok local storage on all nodes:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get pods \ > -n rok-system \ > -l name=rok-disk-manager \ > -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,NODE:.spec.nodeName --no-headers \ > | while read rdm node; do > kubectl exec -n rok-system ${rdm} -- vgs > ${node}-vgs.txt > kubectl exec -n rok-system ${rdm} -- lvs > ${node}-lvs.txt > kubectl exec -n rok-system ${rdm} -- df -h /mnt/data/rok > ${node}-df.txt > doneGet the logs of the Dex Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get svc -n auth dex &> /dev/null \ > && kubectl logs -n auth svc/dex --all-containers > dex.logGet the logs of the AuthService Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl logs -n istio-system svc/authservice --all-containers > authservice.logGet the logs of the Reception Server Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl logs -n kubeflow svc/kubeflow-reception --all-containers > kubeflow-reception.logGet the logs of the Profile Controller Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl logs -n kubeflow svc/profiles-kfam --all-containers > profiles-kfam.logGet the logs of the Cluster Autoscaler Pod:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get deploy -n kube-system cluster-autoscaler &> /dev/null \ > && kubectl logs -n kube-system deploy/cluster-autoscaler --all-containers > cluster-autoscaler.logGet Services in all namespaces:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get svc -A -o wide > services.txtroot@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# kubectl get svc -A -o yaml > services.yamlSet the tarball name:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# export TARBALL=$(realpath ~/${NAME}.tar.gz)Create tarball:
root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# env GZIP=-1 tar -C ${WORKDIR?} -czvf ${TARBALL?} ${NAME?}Find the tarball under
$HOME. Copy the output to your clipboard, as you are going to use it later:root@rok-tools:~/ops/ekf-logs# cd && echo ${TARBALL?} /root/ekf-logs-20211221-155217.tar.gz
What’s Next¶
The next step is to send the tarball to the Arrikto Support Team.
