Use GPU Jupyter Images¶
This section will guide you through creating a new notebook server using one of our GPU-enabled images.
Overview
What You’ll Need¶
- An Arrikto EKF or MiniKF deployment.
Procedure¶
Create a new notebook server.
Use the following Kale Docker image:
gcr.io/arrikto/jupyter-kale-gpu-py38:<IMAGE_TAG>Note
The
<IMAGE_TAG>varies based on the MiniKF or EKF release.This image comes with the CUDA toolkit pre-installed.
Enter the number of GPU devices you need in the
GPUssection of the Jupyter Web App: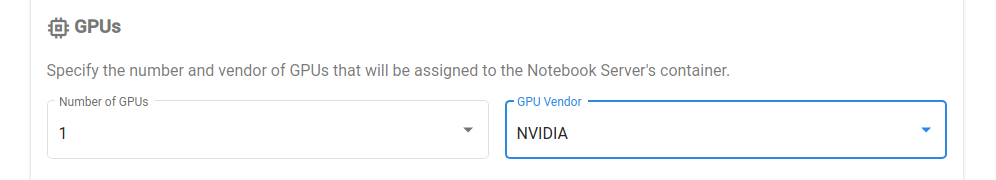
Create a new notebook server.
Use the following Kale Docker image:
gcr.io/arrikto/jupyter-kale-gpu-tf-py38:<IMAGE_TAG>Note
The
<IMAGE_TAG>varies based on the MiniKF or EKF release.This image is using the GPU generic one as its base image, adding the following libraries:
- cuDNN
- cuBLAS
- cuFFT
- cuSPARSE
- cuRAND
- cuSOLVER
- NVRTC
Enter the number of GPU devices you need in the
GPUssection of the Jupyter Web App:
Create a new notebook server.
Use any of the Jupyter Kale images. For example:
gcr.io/arrikto/jupyter-kale-py38:<IMAGE_TAG>Note
The
<IMAGE_TAG>varies based on the MiniKF or EKF release.Enter the number of GPU devices you need in the
GPUssection of the Jupyter Web App:
Start a new terminal inside the notebook server.
Install the CUDA version of PyTorch:
jovyan@gpu-0:~$ pip3 install torch==1.10.0+cu113 \ > -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113/torch_stable.htmlPyTorch bundles all the CUDA libraries as part of its PyPI package, so no system-level libraries are required.
Note
Please head to the PyTorch website for the latest releases.
Verify¶
Start a new terminal inside your notebook server.
Verify that the notebook can consume the GPU devices you requested:
jovyan@gpu-0:~$ nvidia-smi +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 460.73.01 Driver Version: 460.73.01 CUDA Version: 11.2 | |-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ | GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | | | | MIG M. | |===============================+======================+======================| | 0 Tesla K80 Off | 00000000:00:04.0 Off | 0 | | N/A 33C P8 26W / 149W | 0MiB / 11441MiB | 0% Default | | | | N/A | +-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Processes: | | GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory | | ID ID Usage | |=============================================================================| | No running processes found | +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+You should get an output similar to the above.
Start a new notebook (IPYNB file) from inside your notebook server.
Verify that TensorFlow can consume the GPU devices:
import tensorflow as tf tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')You should see an output similar to:
[PhysicalDevice(name='/physical_device:GPU:0', device_type='GPU')]
Start a new notebook (IPYNB file) from inside your notebook server.
Verify that PyTorch can consume the GPU devices:
import torch torch.cuda.is_available()Which should return
True.
