Open Source Kubeflow Components¶
Open Source Kubeflow (OSS Kubeflow) is a platform and integrated toolkit for Machine Learning (ML) built on Kubernetes. OSS Kubeflow supports ML workflows from data preparation through training and deployment. It enables a scalable pipeline structure that helps ensure containerized steps with defined dependencies. OSS Kubeflow extends Kubernetes’ ability to run independent and configurable systems with a curated set of compatible tools and frameworks specific for ML.
An OSS Kubeflow deployment is
- Portable - Run ML systems across various clouds, local, and on-premises platforms and ensure consistent behavior for experimentation, test, and production use.
- Scalable - Maximize available resources and scale with little manual effort.
- Composable - Compose independent containerized components as steps in a full ML workflow with defined inputs and outputs.
Jupyter Notebook Services¶
OSS Kubeflow deployments include services for spawning and managing Jupyter notebooks. With the Notebook servers component you can use the default Docker image or create custom images to support the dependencies you require. ML frameworks and OSS Kubeflow components provide SDKs that enable you to write code to implement the steps in an ML workflow.
Note
Arrikto Enterprise Kubeflow extends the UI and functionality of Jupyter Notebooks and provides an SDK to enable data scientists to orchestrate most of an ML workflow from within their IDE.
Model Training Operators¶
OSS Kubeflow provides a number of frameworks for training, including MPI, MXNet, PyTorch, TensorFlow, and XGBoost. These are provided as Kubernetes custom resources that enable you to submit jobs to training operators. You can configure the training controller for an operator to use CPUs or GPUs and to suit various cluster sizes. The controller takes care of spinning up and managing all of the individual processes and configuring them to talk to one another.
The Katib Hyperparameter Tuning System¶
Hyperparameters are the variables that control a model training process, including: learning rate, number of layers in a neural network, number of nodes in each layer. Automated hyperparameter tuning works by optimizing a target variable such as the model’s accuracy. Katib runs several training jobs to test different sets of hyperparameter configurations and outputs the optimized values for hyperparameters.
Note
Arrikto Enterprise Kubeflow enables data scientists to configure and run hyperparameter tuning jobs from within their IDE (e.g., Jupyter Notebook), without the need to compose YAML files or have any Kubernetes knowledge.
Pipelines System¶
The OSS Kubeflow Pipelines platform enables you to define an ML workflow, including all the components in the workflow (pipeline) and how they combine to form a directed graph. Note that pipeline components and Kubeflow components are two different concepts:
- A Kubeflow component is one of the platforms, systems, services, or other tools distributed with Kubeflow.
- A pipeline component is self-contained code that performs one step in an ML workflow, such as data preprocessing, data transformation, model training, etc. A pipeline component is analogous to a function, in that it has a name, parameters, return values, and a body.
You must package pipeline components as Docker images. Pipeline components represent a specific program or entry point inside a container. The code for each pipeline component includes the client code and the runtime code. The client code talks to endpoints to submit jobs. Runtime code does the actual job and usually runs in the cluster.
Each component in a pipeline executes independently. You must serialize (to strings or files) all the data pieces that you pass between the components so that the data can travel over the distributed network. You must then deserialize the data for use in the downstream component.
The OSS Kubeflow Pipelines Platform UI enables you to configure and experiment with different runs of a pipeline and compare the results. The platform orchestrates runs of a pipeline launched from the pipelines UI. The UI also enables you to view the output artifacts and logs for each step in a pipeline run for evaluation purposes.
Note
Arrikto Enterprise Kubeflow enables data scientists to automatically create pipelines from code via Python decorators or through a JupyterLab UI. You may also snapshot entire pipelines or individual steps for versioning, sharing, and collaboration. Arrikto Enterprise Kubeflow also features fast and efficient data passing between components.
The Machine Learning Metadata DB¶
As you build and experiment with pipelines, you will want to iterate in an effort to improve performance. The metadata management component of Kubeflow, called the Machine Learning Metadata DB (MLMD) enables users to understand and manage their machine learning (ML) workflows by tracking and managing the metadata that the workflows produce.
In this context, metadata means information about contexts (experiments), executions (runs), models, datasets, and other artifacts. Artifacts are the files and objects that form the inputs and outputs of the components in your ML workflow. MLMD is the basis for providing the complete lineage for any kind of artifact.
Note
Arrikto Enterprise Kubeflow enables data scientists to automatically log contexts, executions, and artifacts as they are building their pipelines without the need to write any MLMD-specific code.
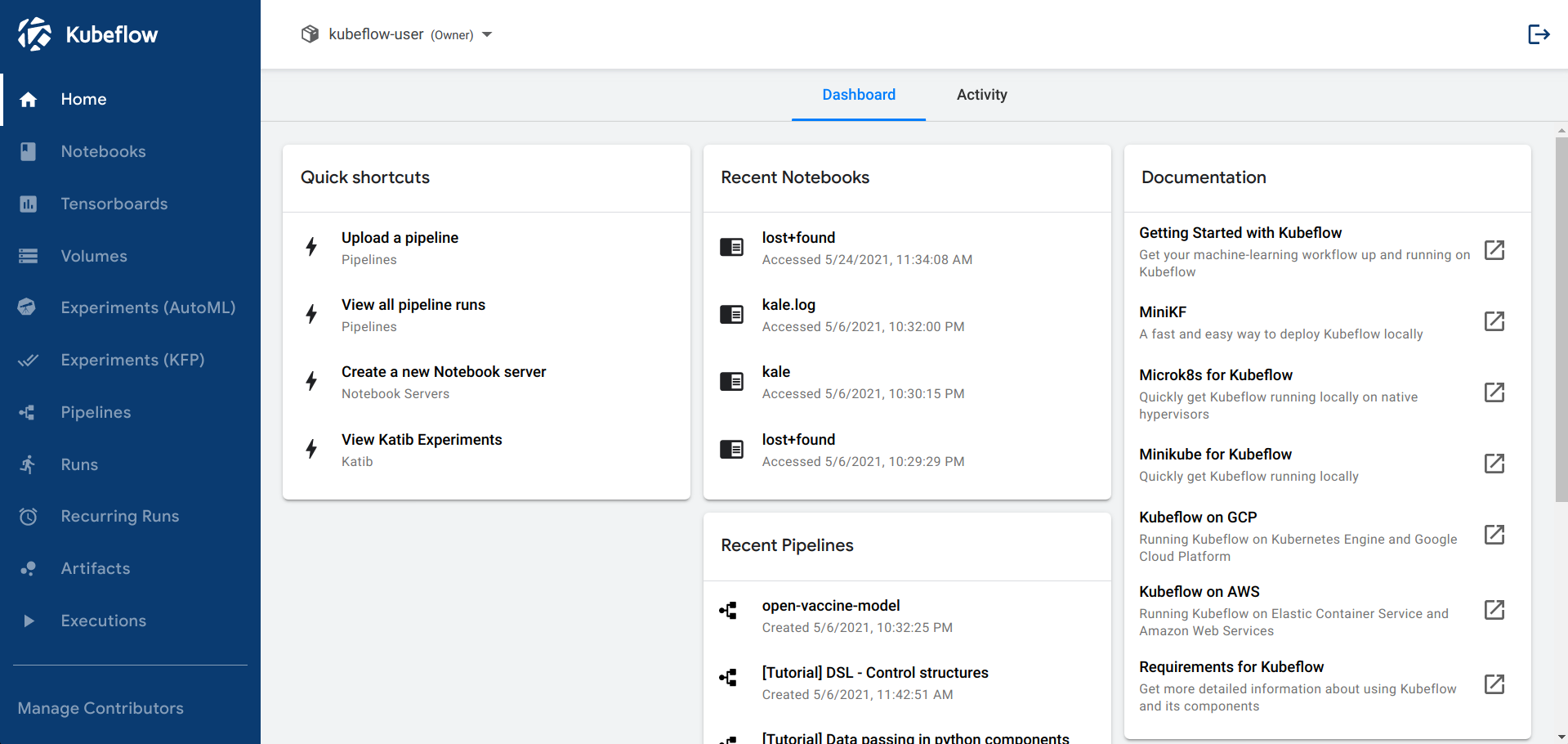
Central Dashboard¶
The central dashboard provides quick access to the Kubeflow components deployed in your cluster. It includes the following features:
- Shortcuts to common actions.
- Lists of recent pipelines and notebooks.
- Metrics that provide an overview of your jobs and cluster in one view.
- A launchpad for the UIs of components running in the cluster, for example, pipelines, notebooks, and the hyperparameter tuning service.
The Kubeflow UIs found in the dashboard include:
- Home, a central dashboard for navigation between the Kubeflow components.
- Pipelines for a Kubeflow Pipelines dashboard.
- Notebook Servers for Jupyter notebooks.
- Katib for hyperparameter tuning.
- Manage Contributors for sharing user access across namespaces in the Kubeflow deployment.
Note
Arrikto Enterprise Kubeflow extends the set of included services and incorporates additional UIs in the Central Dashboard that enable you to access these services.