Invoke Existing InferenceService¶
In this section, you will query an existing InferenceService for
predictions using Kale’s Endpoint API.
Overview
What You’ll Need¶
- An Arrikto EKF or MiniKF deployment with the default Kale Docker image.
- An
InferenceServicedeployed in your namespace, for example, the one created after completing the Serve Scikit Learn Models guide.
Procedure¶
Note
The procedure below serves as an example for the InferenceService you
deployed in the Serve Scikit Learn Models guide. If you want to use
your own InferenceService, adjust the code accordingly.
Navigate to the Models UI to retrieve the name of the
InferenceService. In our example, this will besklearn-tutorial.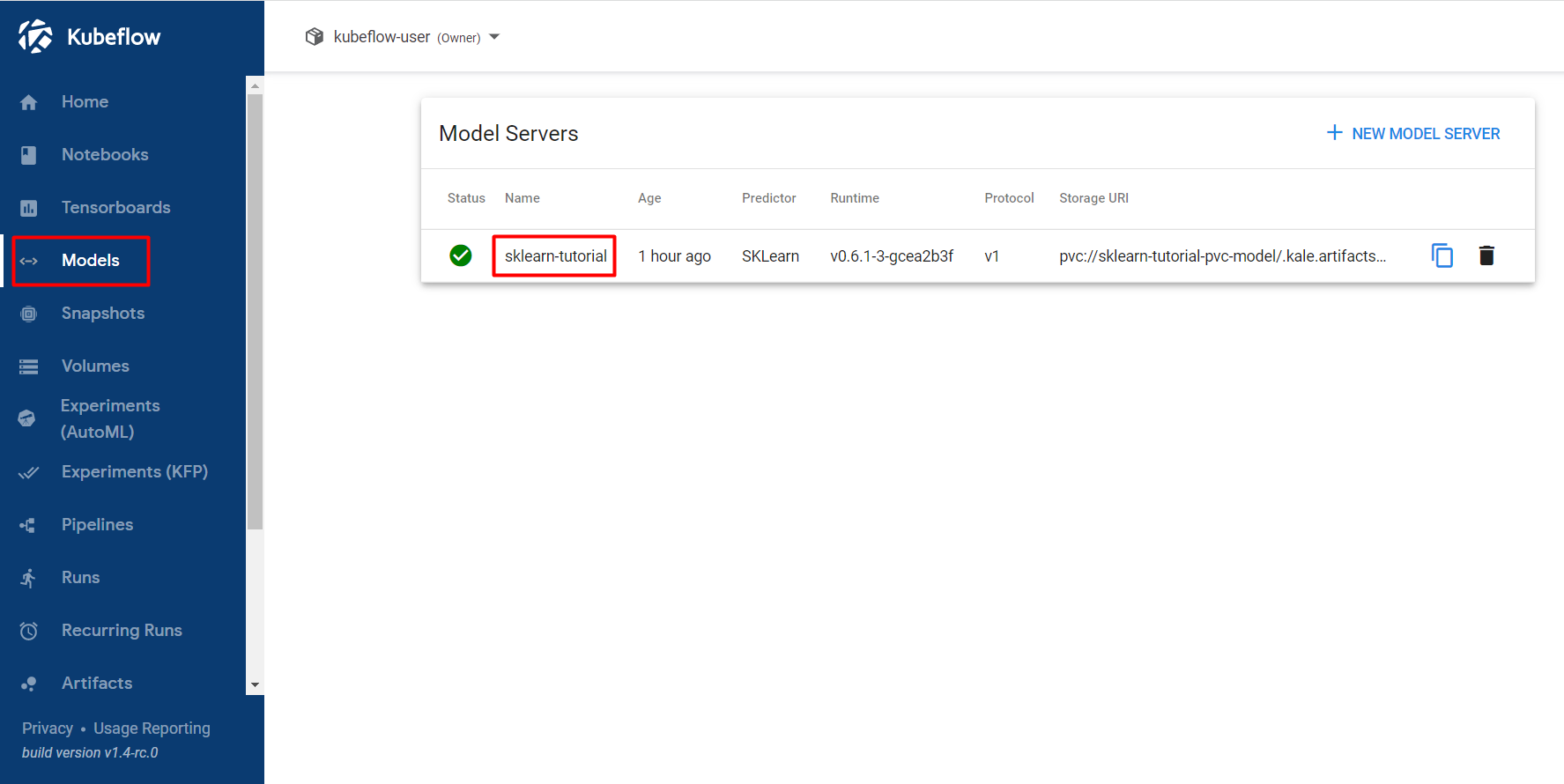
Create a new notebook server using the default Kale Docker image. The image will have the following naming scheme:
gcr.io/arrikto/jupyter-kale-py38:<IMAGE_TAG>Note
The
<IMAGE_TAG>varies based on the MiniKF or Arrikto EKF release.Create a new Jupyter notebook (that is, an IPYNB file):

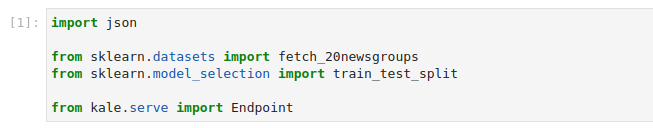
Copy and paste the import statements in the first code cell, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:
In a different code cell, fetch the dataset, and split it into train and test sets. Copy and paste the following code, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:

In a different code cell, initialize a Kale
Endpointobject using the name of theInferenceServiceyou retrieved in the previous step. Then, run it:Note
When initializing an
Endpoint, you can also pass the namespace of theInferenceService. If you do not provide one, Kale assumes the namespace of the notebook server.This is how your notebook cell will look like:

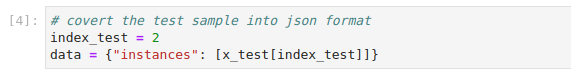
Prepare the data payload for the prediction request. Copy and paste the following code in a new cell, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like:
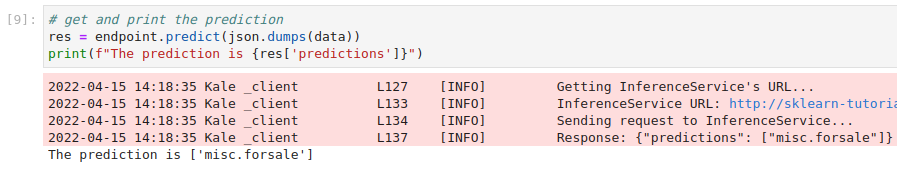
Invoke the server to get predictions. Copy and paste the following snippet in a different code cell, and run it:
This is how your notebook cell will look like: